Figure 1.
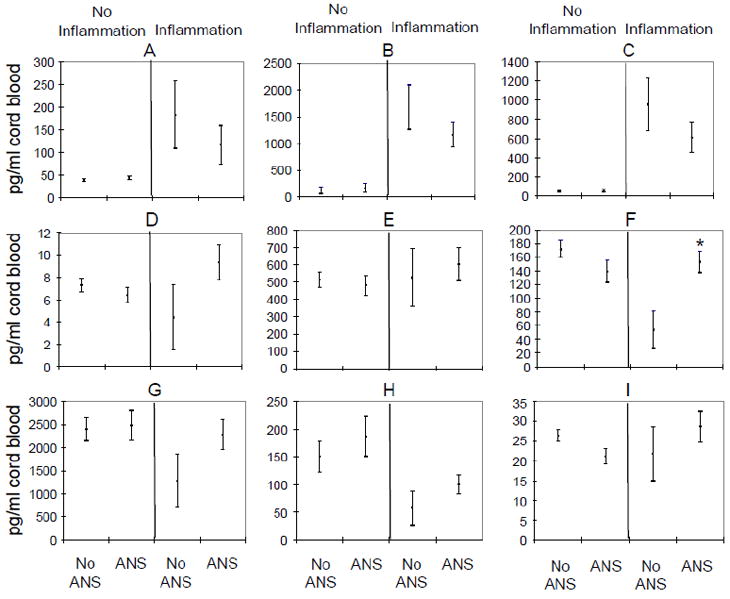
Effect of antenatal steroid exposure on cord blood cytokine concentrations in infants with and without evidence of placental inflammation.
Cord blood concentrations of IL-1β (A), IL-6 (B), IL-8 (C), IL-4 (D), IL-10 (E), TGFß (F), BDNF (G), NT-3 (H), and NT-4 (I) are presented as mean ± standard deviations and normalized for 1 minute Apgar score ≤3 and gestational age. 133 infants had no evidence of placental inflammation, 83 of these 133 infants had no ANS and 50 infants had ANS. 67 infants had evidence of placental inflammation and 17 of these infants had no ANS and 50 had ANS. Cytokine concentrations were compared for infants with ANS exposure and without ANS exposure in each subgroup of infants with and without evidence of placental inflammation. * = p value <0.05, (Using linear regression and adjustment for 1 minute Apgar ≤ 3 and gestational age at birth, TGF-β levels were significantly lower in infants with placental inflammation and no ANS compared to infants with placental inflammation and ANS)
