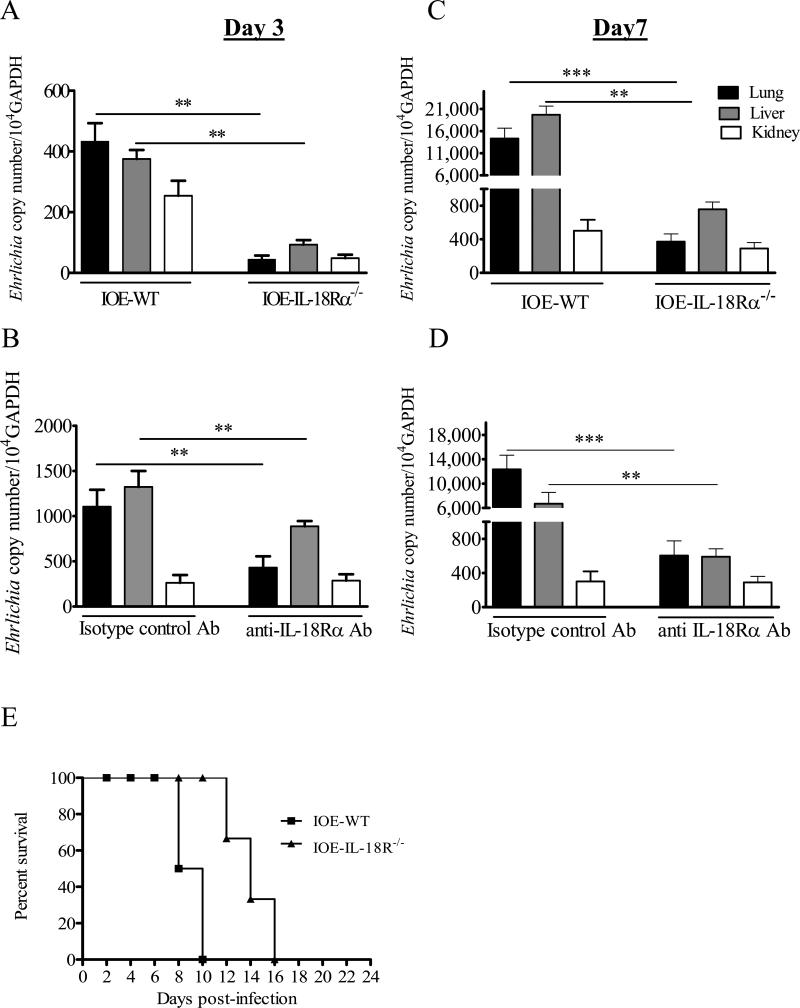
FIGURE 3. Enhanced resistance to IOE infection in IL-18Rα-/- and anti-IL-18Rα -mAb treated mice compared to infected WT or sham control mice.
C57BL/6 WT and IL-18Rα-/- mice (A and C) or anti-IL-18Rα-/- antibody-treated mice and isotype controls (B and D) were infected via the i.p. route with a high dose of IOE (i.e. lethal infection). On days 3 (A and B) and 7 (C and D) p.i., tissues from lung, liver, and kidney were collected and bacterial burden was determined by real time PCR using the second primer set. The copy number of IOE was normalized to the housekeeping gene GAPDH. Bacterial burden in all organs were lower in IOE-infected IL-18Rα-/- and anti-IL-18Rα mAb treated mice compared to WT and isotype controls on days 3 and 7 p.i. The data represent the mean ± SEM of three mice/ group. The data are representative of three independent experiments with similar results. *P <0.05, **P< 0.01. , ***P< 0.001. E, Survival of WT and IL-18Rα-/- mice over 24 days after i.p. infection with high dose of IOE. The data shown represent one of three independent experiments with a total of 12 mice/group.