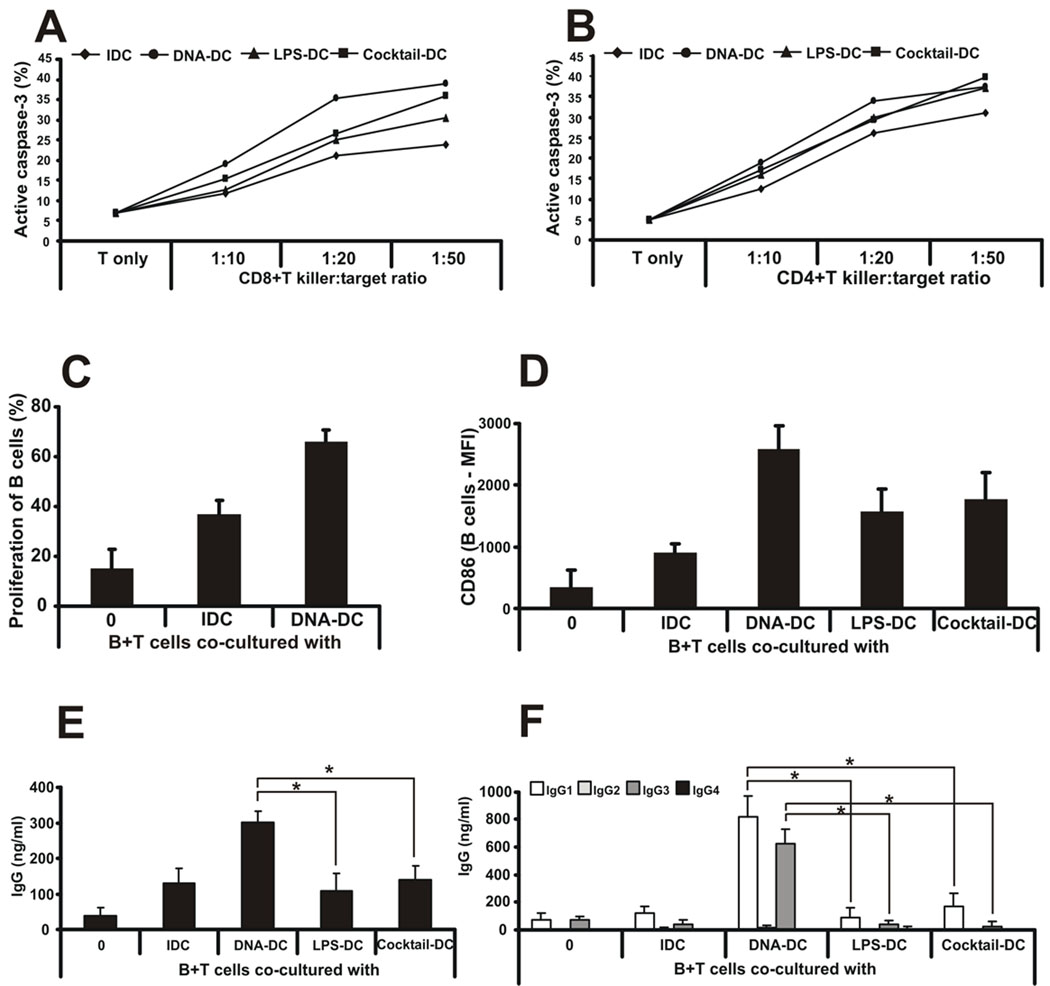
Figure 3. dsDNA-activated DCs confer killing ability on CD4+ and CD8+ T cells and collaborate with T cells to generate a specific humoral response.
A, Oku-1 cells were co-cultured with naïve CD8+ or B, CD4+ T cells and differentially activated DCs for 4 days at different killer:target ratios (from 1:10 to 1:50). To measure the killing capacity of DC-activated T cells, fresh, CFSE-labeled Oku-1 cells were added to the co-cultures for an additional 4h. To identify apoptotic target cells, flow cytometry was used to detect intracellular active caspase-3 in CFSE-positive cells. n=5 independent experiments. One representative data set is shown. C, Allogeneic B cells were co-cultured with IDCs or poly(dA:dT)-activated DCs and cell proliferation was measured by CFSE labeling. Proliferation is shown as percentage of cells with low CFSE staining. D, Allogeneic B cells were co-cultured with IDCs or poly(dA:dT)-, LPS- or inflammatory cytokine cocktail-activated DCs and the surface expression of CD86 molecule was measured by flow cytometry. E, Allogeneic B and T cells were co-cultured with IDCs or poly(dA:dT)-, LPS- or inflammatory cytokine cocktail-activated DCs and total immunoglobulin G production was measured from the supernatants. F, Immunoglobulin G subclass profiling was done from co-culture supernatants by ELISA. n=3 independent experiments.