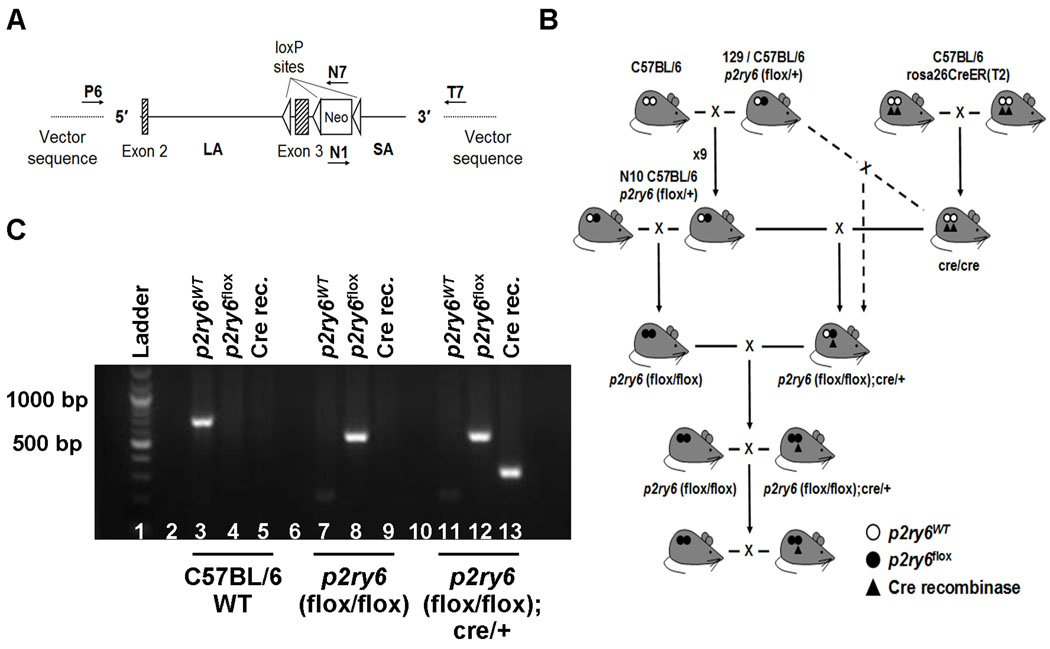
Figure 1. Generation of +/+ and p2ry6 (flox/flox);cre/+ mice.
(A) The conditional gene-targeting vector was obtained from an ~12.7 kb B6 bacterial artificial chromosome subclone and contained a long homology arm (LA; 9.6 kb), p2ry6 exons 2 and 3, the latter flanked at the 5′ side by a single loxP site and at the 3′ side by a PKG-neo cassette with loxP and FRT sites, and a short homology arm (SA; 2.1 kb). The target region was ~1.8 kb and included exon 3. The annealing sites of the primers used to confirm the structure of the vector are indicated as P6, N7, N1, and T7. (B) Schematic representation of the breeding protocol used to generate +/+ and p2ry6 (flox/flox);cre/+ mice. p2ry6 (flox/flox) mice on a C57BL/6 × 129 mixed background (dashed line) or on a C57BL/6 background (solid line) were initially mated with cre/cre mice to generate +/+ and p2ry6 (flox/flox); cre/+ strains. (C) PCR amplification products of the wild-type (p2ry6WT) and floxed (p2ry6flox) p2ry6 gene and of the Cre recombinase in C57BL/6 wild-type (lanes 3–5), p2ry6 (flox/flox) (lanes 7–9) and p2ry6 (flox/flox);cre/+ (lanes 11–13) mice, resolved on a 2% agarose gel.