Figure 3.
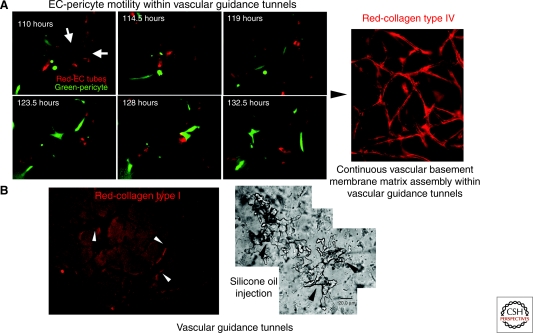
Vascular guidance tunnels: ECM conduits generated during vessel tubulogenesis that regulate EC-pericyte interactions, ECM remodeling, vascular basement membrane matrix assembly, and vessel stabilization. The process of EC tubular morphogenesis in 3-D collagen matrices leads to the creation of networks of EC-lined tubes, and also networks of vascular guidance tunnels in which ECs reside. The tunnels are formed during lumen and tube formation through EC cell surface proteolysis by MT1-MMP. EC-lined tubes within vascular guidance tunnels recruit pericytes to the tube ablumenal surface; subsequently, pericytes migrate along this surface within the tunnels. (A) Time-lapse imaging of EC tubes (RFP-labeled) and pericytes (GFP-labeled) reveals motility of pericytes along the tube ablumenal surface over time. Arrows indicate EC tube ablumenal surface. Bar equals 25 µm. Active motility of pericytes along tubes leads to EC-pericyte interactions and contributions of basement membrane components, such as collagen type IV, which is deposited continuously along the ablumenal surface (right panel; Bar equals 50 µm). (B) Vascular guidance tunnels are formed during EC tubulogenesis through MT1-MMP-mediated proteolysis and can be shown using anticollagen type I antibodies (left panel; Bar equals 50 µm; the tunnels are the negative stained areas; arrowheads indicate tunnel borders) or by microinjection of tunnels with silicone oil (right panel; Bar equals 20 µm; arrowheads indicate tunnel borders).