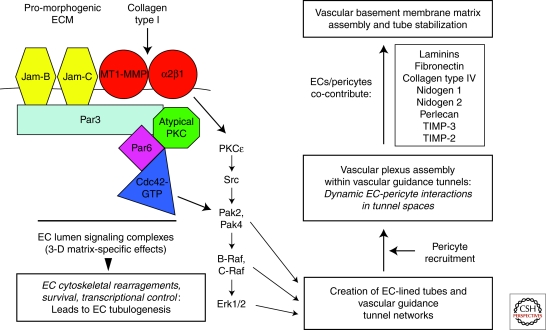
Figure 4.
Molecular signaling events controlling vascular tube morphogenesis, matrix remodeling, and stabilization in 3-D extracellular matrices. Multicomponent signaling complexes control EC lumen and tube formation in 3-D matrices. A key aspect of this mechanism is the integration of Cdc42-mediated signaling with cell surface proteolysis through MT1-MMP. A downstream kinase signaling cascade is activated leading to EC cytoskeletal changes, survival, and transcriptional control that regulates EC tubular morphogenesis. EC tube formation leads to the generation of networks of vascular guidance tunnel spaces within the ECM that are occupied by ECs, thereby allowing for EC motility and remodeling events (illustrated in Fig. 3). Pericytes are recruited to these EC-lined tunnels and EC-pericyte motility within these tunnels and along the tube ablumenal surface leads to ECM remodeling and vascular basement membrane matrix assembly. Both ECs and pericytes have been shown to contribute basement membrane matrix components (illustrated in Fig. 5), as well as TIMP-2 and TIMP-3, which together control the formation and stability of the vascular basement membrane.