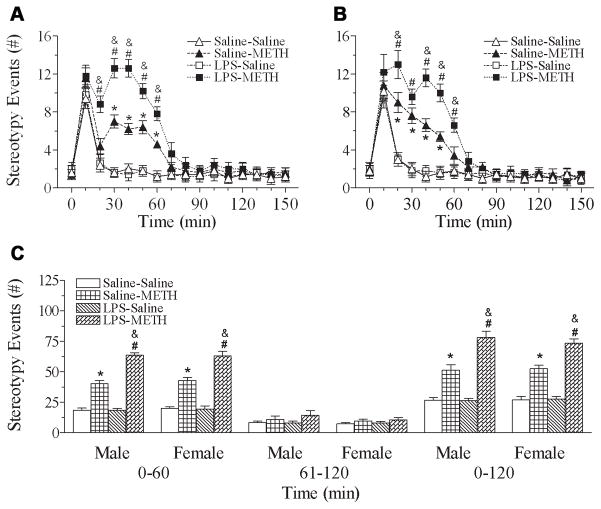
Fig. 5.
Effect of neonatal LPS-exposure on METH-induced stereotyped behaviors in the P70 male (A) and female (B) rats. A & B, average values for stereotyped behaviors by the P70 rats after saline or METH (0.5 mg/kg) treatment. Each point represents the cumulative stereotyped behaviors determined at the first minute of every 10-min intervals during 150 min. C, bar graphs represent the average values for stereotyped behaviors by P70 rats in specific time intervals from 0 to 60 min, 61 to 120 min, and 0 to 120 min, after saline or METH (0.5 mg/kg) treatment. The results are expressed as the mean±SEM of five animals in each group and analyzed by two-way repeated measures ANOVA for data from tests conducted continuously at different experimental times or by two-way ANOVA for the behavioral response in the specific time intervals followed by Student-Newman-Keuls test. * P<0.05 represents significant difference for the saline+METH group as compared with that of the saline+saline group. # P<0.05 represents significant difference for the LPS+METH group as compared with that of the LPS+saline group. & P<0.05 represents significant difference for the LPS+METH group as compared with that of the saline+METH group.