Fig. 6.
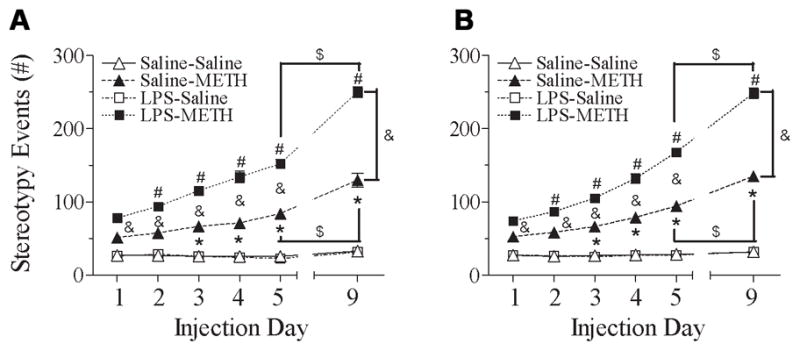
Effect of neonatal LPS-exposure on METH-induced behaviors sensitization (from P70 to P74) and reinstated behaviors sensitization (P78), as determined by stereotyped behaviors in the male (A) and female (B) rats. Repeated administration of METH in rats developed behavioral sensitization as indicated by the progressively increased behavioral response of the stereotyped behaviors as compared with the data of day 1 (P70). After 5 injections from P70 to P74 (day 1 to day 5), animals received a single injection of saline or METH after ninety-six hour drug withdrawal from the 5th injection of METH to assess the reinstated behavioral sensitization (P78, day 9). Each point represents the cumulative stereotyped behaviors of 120 min (first minute of every 10-min intervals during 120 min) on the different experimental day. The results are expressed as the mean±SEM of five animals in each group and analyzed by two-way repeated measures ANOVA for data from tests conducted continuously at different experimental day followed by Student-Newman-Keuls test. * P<0.05 represents significant difference for the experimental day as compared with the data of day 1 in the saline+METH group. # P<0.05 represents significant difference for the experimental day as compared with the data of day 1 in the LPS+METH group. & P<0.05 represents significant difference for the LPS+METH group as compared with that of the saline+METH group in the same experimental day. $ P<0.05 represents significant difference for the day 9 as compared with the data of day 5 in the saline+METH or LPS+METH group.
