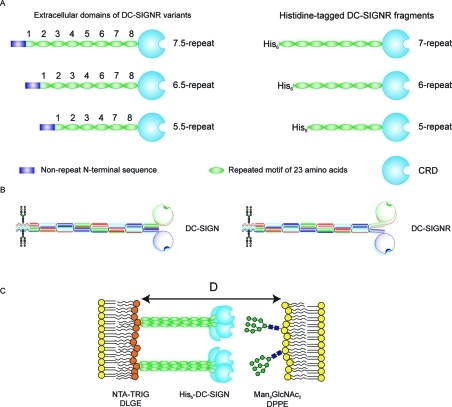
Figure 1.
Organization of the extracellular domain of DC-SIGNR. (A) Length variants of DC-SIGNR (left) and corresponding truncated, His6-tagged proteins used for force–distance measurements (right). (B) Comparison of proposed organization of DC-SIGN and DC-SIGNR based on crystal structures of DC-SIGNR fragments.(17) (C) Configuration of DC-SIGNR and neoglycolipid in force measurements. D is the absolute separation between the bilayer surfaces.