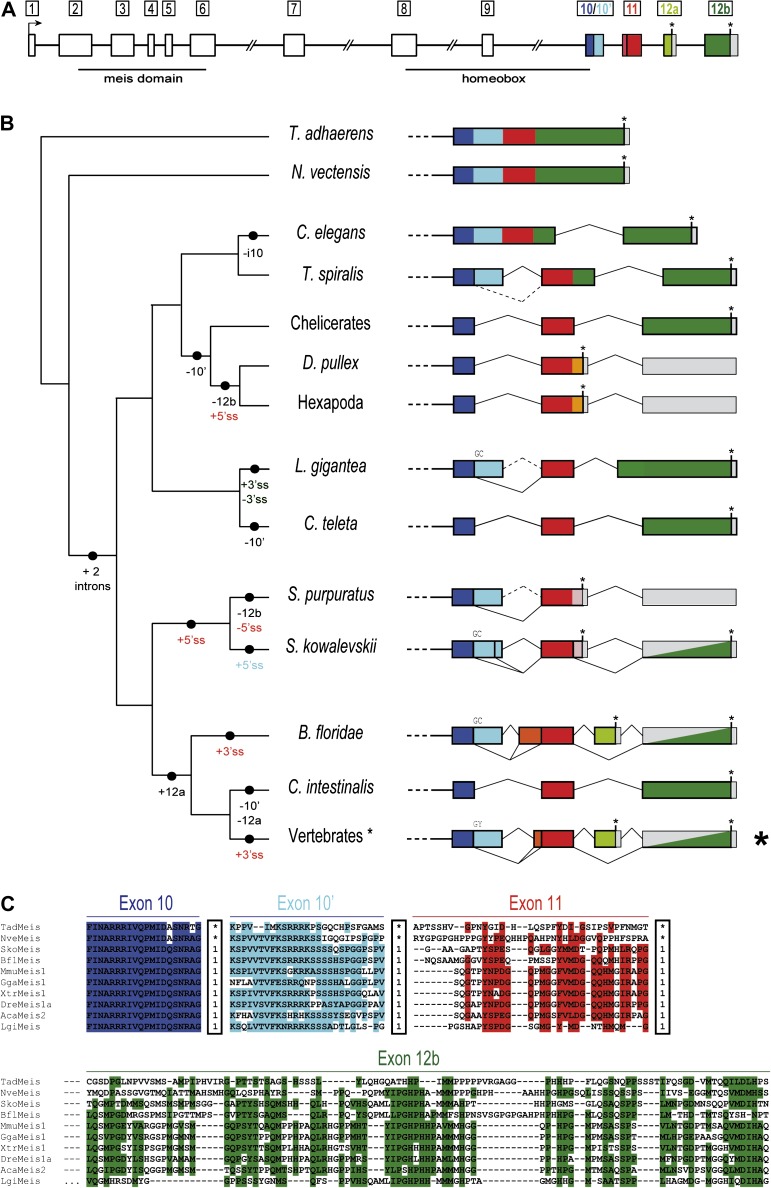
FIG. 1.
Evolution of the intron–exon structures of the C-termini of Meis/hth. (A) Schematic representation of the intron–exon structure of a prototypical vertebrate Meis gene. The conserved long size of introns 6–9 are indicated by a double slash. Homologous coding regions (exons) in the 3′ are indicated by colors: 10 (dark blue), 10′ (light blue), 11 (red), 12a (light green), and 12b (dark green). (B) Diversity of intron–exon structures of exons 10–12b in metazoans. The different genomic gains (+) and losses (−) of regions or splice sites (5′ splice site (SS) or 3′ ss, colored according to the exon), assuming parsimony, are indicated in the branches of the schematic tree on the left-hand side. Solid vertical bars between colors represent a conserved 5′ ss, and GC 5′ ss are indicated above each line. Asterisks represent termination codons and gray blocks indicate UTR exons. Split gray/colored boxes indicate regions that are either translated or 3′ UTR depending on splice form. (C) Sequence alignment for some representative bilaterians and the two non-bilaterians showing sequence conservation at each exon. Within the boxes, “1” indicates a phase 1 intron, and an asterisk represents absence of an intron at that position. Highlighted positions correspond to 60% of similar amino acid types across studied genes, as generated by BioEdit.