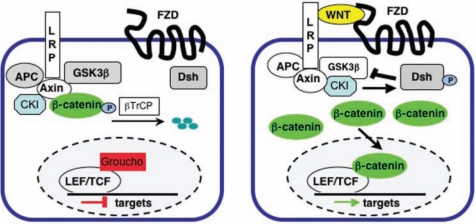
Figure 1.
Simplified schematic of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. (Left) In the absence of a WNT ligand, cytoplasmic β-catenin is associated with APC and Axin, phosphorylated by GSK3β and CKI, and polyubiquitinated by the βTRCP complex, targeting it for proteosomal degradation; under these conditions, LEF/TCF transcription factors in the nucleus associate with transcriptional co-repressors, such as Groucho, and the transcription of Wnt target genes is repressed. (Right) In the presence of a WNT ligand, phosphorylation and degradation of β-catenin are inhibited, allowing it to accumulate in the cytoplasm and translocate into the nucleus. Nuclear β-catenin interacts with LEF/TCF family transcription factors and several other transcriptional co-activators to initiate transcription of target genes. Abbreviations: FZD, Frizzled; LRP, low-density lipoprotein-receptor-related protein; APC, adenomatous polyposis coli; GSK, glycogen synthase kinase; CKI, casein kinase I; DSH, Disheveled; LEF/TCF, Lymphoid enhancer factor/T-cell factor.