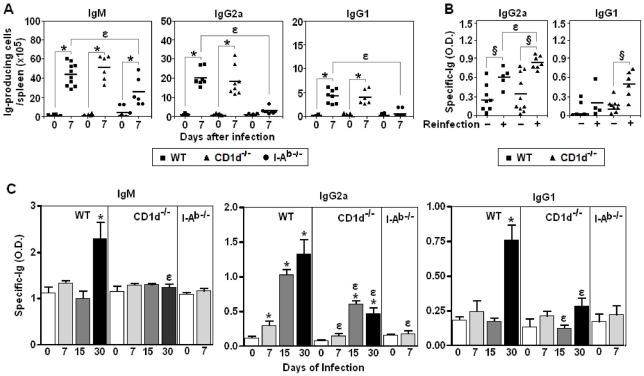
Figure 6. Polyclonal and parasite-specific antibody responses in P. chabaudi-infected WT, CD1d-/- and I-Ab-/- mice.
(A) Total numbers of IgM-, IgG1- and IgG2a-producing cells in the spleen on days 0 and 7 of infection. Each point corresponds to a single mouse. Horizontal lines represent the means of numbers of Ig-producing cells per spleen (n = 6–8). (B) On day 30 p.i., mice were reinfected with 1 × 108 iRBC. Non-reinfected mice were used as controls. The serum levels of parasite-specific IgG2a and IgG1 antibodies were measured 15 days after re-infection (on day 45 p.i.). To favour high-affinity Ig binding, serum samples were incubated with plate-bound parasite antigens during a short period of time (90 min). Each point corresponds to a single mouse. Horizontal lines represent the means of O.D. values (n = 5–10). (C) Serum levels of parasite-specific IgM, IgG2a and IgG1 antibodies were measured on days 0, 7, 15 and 30 of infection. To favour low-affinity Ig binding, serum samples were incubated with plate-bound parasite antigens during a long period of time (overnight). Data represents the means ± SD (n = 4–8). In A, *, p<0.05, infected mice compared with non-infected mice. In A and B, ε, p<0.05, CD1d-/- or I-Ab-/- mice compared with WT mice. In B, §, p<0.05, reinfected mice compared with non-reinfected mice. Data in panel B were statistically different from those of non-infected mice, with the exception of IgG1 O.D. values in non-reinfected mice. Data are representative of three experiments.