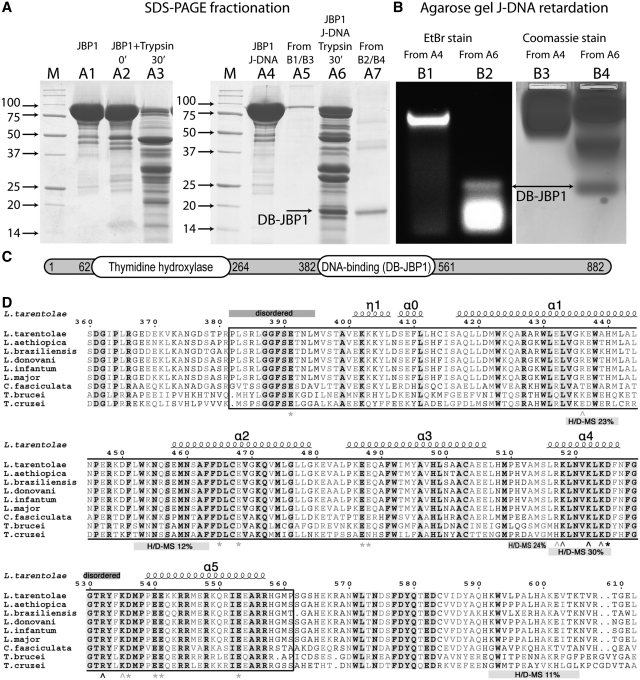
Figure 2.
Identification of the DB-JBP1 domain. (A) SDS–PAGE separation before and after limited proteolysis of the Cf-JBP1 protein alone and bound to J-DNA; the JBP1 and DB-JBP1 bands recovered after elution from the gel after the retardation assay are also shown and DB-JBP1-1is indicated by arrows. (B) Agarose gel DNA mobility retardation assay for JBP1 mixed with J-DNA before and after limited proteolysis, stained with ethidium bromide and with Coomassie blue; DB-JBP1 is indicated by arrows. (C) A schematic drawing of the JBP1 sequence with the N-terminal thymidine hydroxylase domain and the DB-JBP1 domain indicated. (D) A multiple sequence alignment of JBP1 from Leishmania, Trypanosoma and Crithidia; the DB-JBP1 domain is boxed; fully conserved residues are in black and bold on a gray background; conserved residues are in gray and bold; the secondary structure elements and residue numbers correspond to the L. tarantolae protein; disordered regions and peptides identified to be in contact with DNA in the HDX-MS experiment are annotated with labeled bars; wedge indicate Lys/Arg mutations and asterisks indicate D/E mutations (gray for no effect, black for affecting DNA binding).