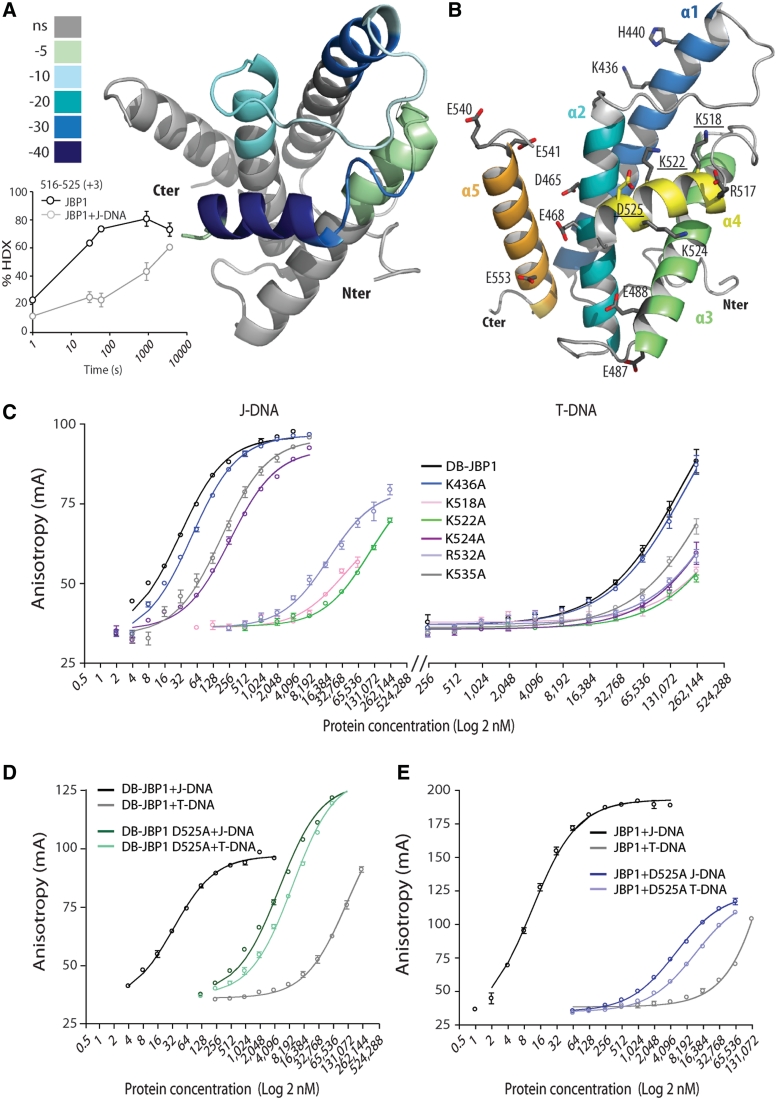
Figure 4.
Mapping the DB-JBP1 regions that bind DNA. (A) The peptides that show hydrogen–deuterium exchange rate differences upon J-DNA binding are colored according to the magnitude of the differences and mapped in the DB-JBP1 structure; the insert depicts the change in hydrogen–deuterium exchange rate of the JBP1 peptides 516–525 (which corresponds to the recognition helix α4) in the unbound and J-DNA bound state. (B) Location of the DB-JBP1 point mutants used to identify the residues involved in J-DNA binding. (C) Binding of varying concentrations of the various Arg/Lys mutants of DB-JBP1 to J-DNA (left) and T-DNA (right); colors are used purely to indicate the different curves more clearly. (D) Binding of DB-JBP1 and (E) JBP1 and the corresponding D525A mutants to T-DNA and to J-DNA.