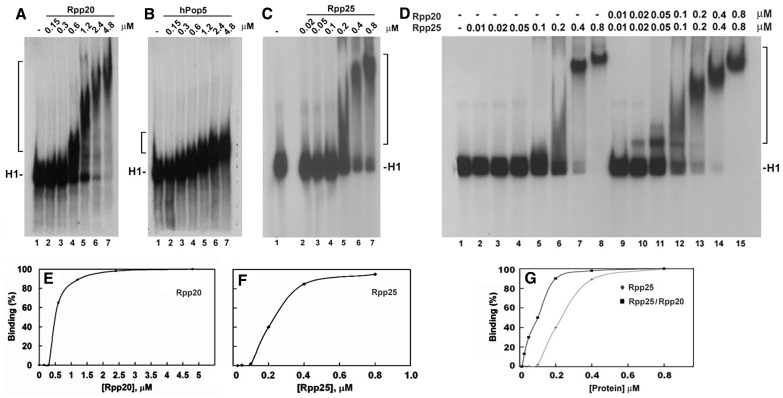
Figure 3.
Rpp20, Rpp25 and Pop5 bind to H1 RNA in gel shift assays. (A–C) Increasing concentrations (in µM) of Rpp20, Pop5 and Rpp25 were incubated with 32P-labeled H1 RNA (5000 cpm) and the formation of complexes was analyzed in 4% native gel and visualized by autoradiography (upper panel; see ‘Materials and Methods’ section). Rpp20 and Rpp25 form monomers and oligomers thus generating large complexes. H1 RNA appears as two bands in native gels (see C, lane 1) but both bands were shifted as one complex in the presence of Rpp25. (D) A gel shift assay using H1 RNA (lane 1) and increasing concentrations of Rpp25 alone (lanes 2–8) or in combination with Rpp20 added at indicated equimolar ratios (lanes 9–15). Proteins were pre-incubated for 30 min before addition of H1 RNA. Complexes are indicated by a bracket. (E and F) Quantitation of H1 RNA–Rpp20 and H1 RNA–Rpp25 complexes, which include single and multiple proteins bound to H1 RNA (37). The K1/2 was calculated as the protein concentration at which 50% binding of protein to H1 RNA was seen. (G) Quantitation of Rpp25/H1 RNA and Rpp20/Rpp25/H1 RNA complexes seen in (D).