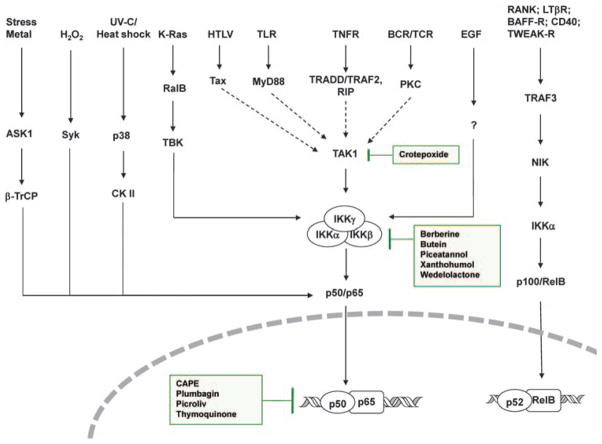
Figure 1.
Signaling network of NF-κB activation in cancer. Various pathways of NF-κB activation in cancers are shown. The sites of action of some phytochemicals are also indicated in the boxes. The network converges at three major sites (IKK kinase such as TAK1, IKK itself and the p50–p65 heterodimer). ASK1, apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1; BAFF-R, TNF family member B cell-activating factor-receptor; CK II, casein kinase II; HTLV, human T-lymphotropic virus; LTβR, lymphotoxin-β receptor; MyD88, myeloid differentiation primary response gene 88; RalB, RAS-like protein B; RANK, receptor activator for nuclear factor κB; RIP, receptor interacting protein; Syk, spleen tyrosine kinase; TAK1, transforming growth factor (TGF)-β activating kinase 1; TBK, TRAF family member-associated NF-κB activator (TANK)-binding kinase; TLR, toll-like receptor; TNFR, tumor necrosis factor receptor; TRADD, TNFR1-associated death domain; TRAF, TNF-receptor-associated factor; β-TrCP, β-transducin repeat-containing protein; TWEAK-R, TNF-related weak inducer of apoptosis-receptor; UV, ultra violet.