Table 2.
Inequity in the use of doctor services - horizontal inequity indices
| 2000 | 2002 | 2005 | 2002 | 2005 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dependent variable a) | (I) | (I) | (I) | (II) | (II) |
| probability of GP visit | 0.0091 | -0.0031 | 0.0050 | 0.0013 | 0.0068 |
| 1.49 | -0.49 | 0.74 | 0.20 | 1.03 | |
| number of GP visits | -0.0109 | 0.0053 | -0.0066 | 0.0207 | 0.0072 |
| -0.78 | 0.37 | -0.38 | 1.48 | 0.41 | |
| probability of private specialist visit | 0.0726 | 0.0496 | 0.0449 | 0.0571 | 0.0472 |
| 3.31 | 2.16 | 1.87 | 2.50 | 1.97 | |
| number of private specialist visits | 0.0612 | 0.0622 | 0.0311 | 0.0781 | 0.0338 |
| 1.23 | 1.59 | 0.72 | 1.94 | 0.77 | |
| probability of outpatient hospital visit | 0.0275 | 0.0143 | -0.0043 | 0.0222 | 0.0036 |
| 1.37 | 0.74 | -0.22 | 1.16 | 0.19 | |
| number of outpatient hospital visits | 0.0381 | -0.0021 | 0.0244 | 0.0129 | 0.0415 |
| 0.81 | -0.07 | 0.79 | 0.43 | 1.36 |
a) Specification (I) uses self-assessed health as the only health need indicator, while (II) includes additional health information. t-values are given in italics below each index. Statistically significant indices at 5% level are shown in bold. Horizontal inequity indices (HI) are based on equations (1)-(3). To compute HI, we apply eq. (1) but replace yi in (1) with 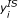 from eq. (3).
from eq. (3).
