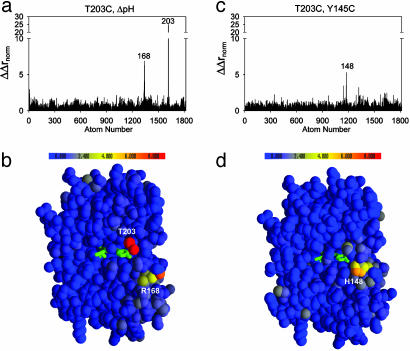
Fig. 4.
Structure cycle analysis shows independent interaction mechanisms for the two-way thermodynamic couplings. Bar graphs (a and c) and colorimetric representations (b and d) of the magnitude of structural coupling (ΔΔrnorm) for each atom in the T203C–ΔpH (a and b) and Y145C–T203C (c and d) cycles. The values report the degree to which each atom feels the effect of one mutation differently when in the background of another mutation and is the structural analog of the double mutant cycle. Despite two-way thermodynamic coupling (Fig. 3) and overlapping structural change (Fig. 2) of the single mutants, the structural cycle analysis predicts that T203C and ΔpH interact through a distinct mechanism from that of the T203C–Y145C pair.