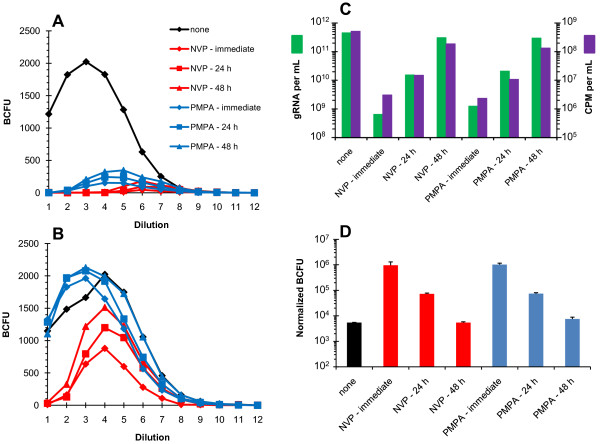
Figure 2.
RTIs can be effectively removed from virus preparations. Env(-) VSV-G pseudotyped WT HIV-1 expressed from 293T cells transfected in the absence (black), or presence of 1.0 mM PMPA (blue) or 50 μM NVP (red), is assayed for limiting-dilution infectivity on TZM-bl cells (panels A, B and D). The numbers on the X-axes (panels A and B) represent the dilution series, each step being a 3-fold serial dilution starting with 0.1 mL of undiluted infectious supernatant (Dilution 1). For each drug treatment, RTIs were added either immediately before transfection, 24, or 48 h after transfection as indicated in the legend at the right of panel A. Blue colony forming units (BCFU) were tallied 48 h after the infectivity experiments were started [41]. Panel A shows the titer of infectious supernatants assayed without PEG precipitation of virus. Panel B shows the titer of infectious supernatants after PEG precipitation to remove RTIs from the virus stock (see legend from panel A). Panel C shows the yield of WT virus from each transfection condition (with or without drugs) measured using either qRT-PCR (quantifying gRNA per mL, green) or exogenous-template RT assays (measuring RT activity in counts per minute of [32P]-TMP incorporated per mL [CPM per mL], purple). Panel D shows the titer of the PEG-precipitated WT virus, with the treatments (indicated at the bottom) normalized for the gRNA present in the starting supernatant (i.e., corrected for dilution). Values are expressed as normalized blue cell forming units (BCFU) and represent the averages from at least three dilutions (error bars indicate standard deviations).