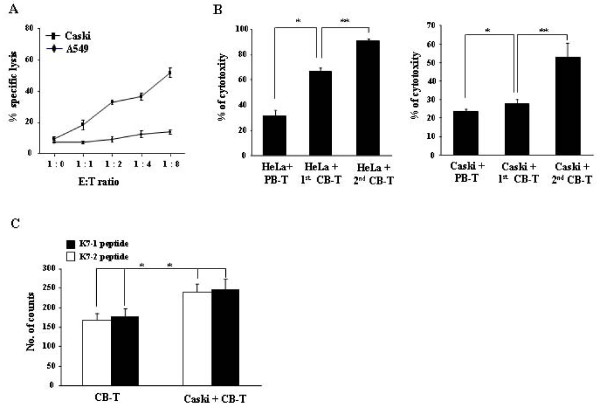
Figure 6.
Cytotoxic activity and detection of cervical tumor specific T cells. A, cervical tumor specific cytotoxic activity was shown. T cells were purified from splenocytes of NOD/SCID mice inoculated with cord blood T cells (CB-T) and Caski tumor cells. The T cells were cocultured with Caski cells, HeLa cells, or A549 cells (human lung cancer cells) as a negative control. Cytotoxicity was tested by flow cytometry with several effector-to-target ratios. B, cytotoxic activity of purified T cells against HeLa (left) and Caski (right) cells was determined for non-adoptive T cells (1st CB-T) and adoptive T cells (2nd CB-T), and human peripheral blood T lymphocytes (PBL-T) as a control. Each bar indicates the mean ± S.D. as determined from the average of quadruplicate wells (* P < 0.01). C, ELISPOT assay for interferon-gamma (INF-γ) production was conducted with E711-20 peptide (YMLDLQPETT) and E786-93 peptide (TLGIVCPI) HPV specific peptides with non-adopted T cells and adopted T cells. Each bar represents the mean ± S.D. as determined (* P < 0.05).