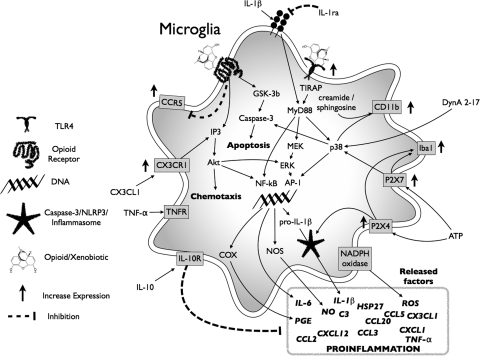
Fig. 4.
Consequences of opioid-induced central immune signaling in microglia. Opioid-induced microglial responses occur via opioid engagement of classic opioid receptors expressed by microglia and via activation of TLR4-dependent signaling. The activation of these signaling events leads to the release of many inflammatory mediators, increased cellular motility and the up-regulation of cell surface receptors that enhance the microglial sentinel role. These classic and nonclassic actions of opioids at microglia result in a profound proinflammatory central immune signaling response that can influence neuronal and non-neuronal cells. If these microglial-dependent events occur in nociceptive control centers of the CNS, such as the dorsal spinal cord, a profound effect on the pharmacodynamics of the administered opioid can be expected (see section III.C for details).