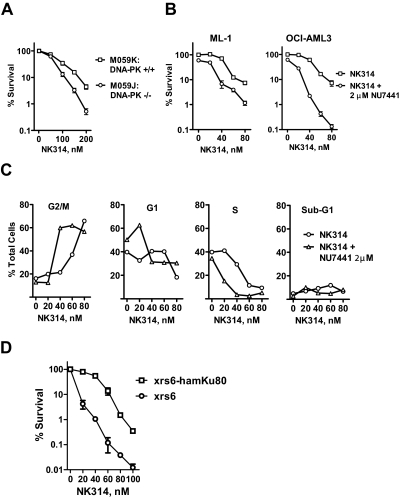
Fig. 2.
DNA-PK complex contributes to cell survival in response to NK314. A, M059J (DNA-PKcs mutant) and M059K (DNA-PKcs wild type) cells were incubated with various concentrations of NK314 for 24 h. Each data point represents the mean ± S.E.M. of triplicate samples. B, ML-1 and OCI-AML3 cells were treated with NK314 in the absence or presence of NU7441, a specific DNA-PK inhibitor. In both experiments, after 24 h, cells were washed and fresh medium was added. Colonies were counted after eight doubling times. Each data point represents the mean ± S.E.M. of triplicate samples. C, ML-1 cells were treated with NK314 in the absence or presence of 2 μM NU7441. Samples were collected at 24 h, stained with propidium iodide, and analyzed by flow cytometry. The data are representative of two independent experiments. D, xrs6 (Ku80-deficient) and xrs6-hamKu80 (Ku80-repleted) cells were treated with 0 to 100 nM NK314 for 24 h. Colonies were counted after 5 days. Each data point represents the mean ± S.E.M. of triplicate samples.