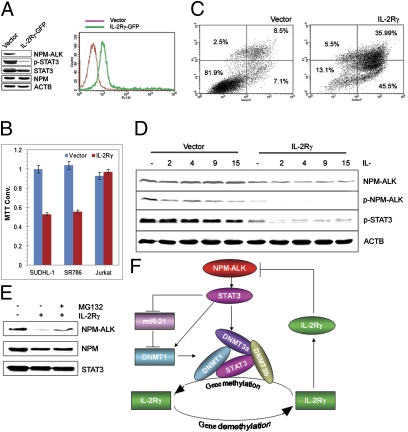
Fig. 6.
IL-2Rγ inhibits NPM-ALK expression and induces apoptosis of ALK+ TCL cells. (A) Transfection efficiency (Right) and impact (Left) of the transfected IL-2Rγ on the expression of NPM-ALK and the other depicted proteins detected by flow cytometry and Western blotting, respectively. (B) Effect of transfected IL-2Rγ on growth of the ALK+ TCL (SUDH-L1 and SR786) and control ALK− TCL (Jurkat) cells. (C) Effect of transfected IL-2Rγ on the apoptotic rate of the ALK+ TCL (SUDHL-1) cells. (D) Effect of IL-2Rγ–signaling cytokines on NPM-ALK expression in the vector or IL-2Rγ–transfected SUDHL-1 cells. (E) Effect of proteosome inhibitor MG132 on NPM-ALK expression in the IL-2Rγ–transfected SUDHL-1 cells. (F) Schematic diagram of NPM-ALK and IL-2Rγ expression regulation loop. STAT3 activated by the oncogenic NPM-ALK tyrosine kinase induces DNMT1 expression by activating DNMT1 gene transcription (25) and inhibition of miR-21 expression. STAT3, DNMT1, DNMT3a, and DNMT3b bind to the IL-2Rγ gene promoter and foster the promoter's silencing. Expression of IL-2Rγ protein induced by demethylation of the IL-2Rγ gene inhibits NPM-ALK expression.