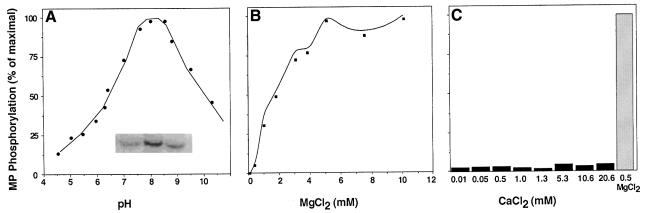
Fig. 2. Effects of pH, Mg2+ and Ca2+ on MP phosphorylation. (A) Effect of pH. The cell wall preparation was dialyzed against 0.1 M citrate buffer pH 4.0–5.5, HEPES pH 6.0–7.5, Tris–HCl pH 8.0–9.0 or borate pH 9.5–10.5 supplemented in each case with 5 mM MgCl2. Each dialyzed sample was then assayed for its ability to phosphorylate MP. Inset (from left to right): MP phosphorylated at pH 5.0, 8.0 and 11.0, respectively. (B) Effect of MgCl2. MP phosphorylation was assayed in the pH 8.0 reaction buffer supplemented with the indicated concentrations of MgCl2. (C) Effect of CaCl2. MP phosphorylation was assayed in the pH 8.0 reaction buffer supplemented with the indicated concentrations of CaCl2. For a positive control, 5 mM MgCl2 was used. The degree of MP phosphorylation was quantified based on analysis of the gel area corresponding to the phosphorylated protein band, using a Molecular Dynamics phosphorimager.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.