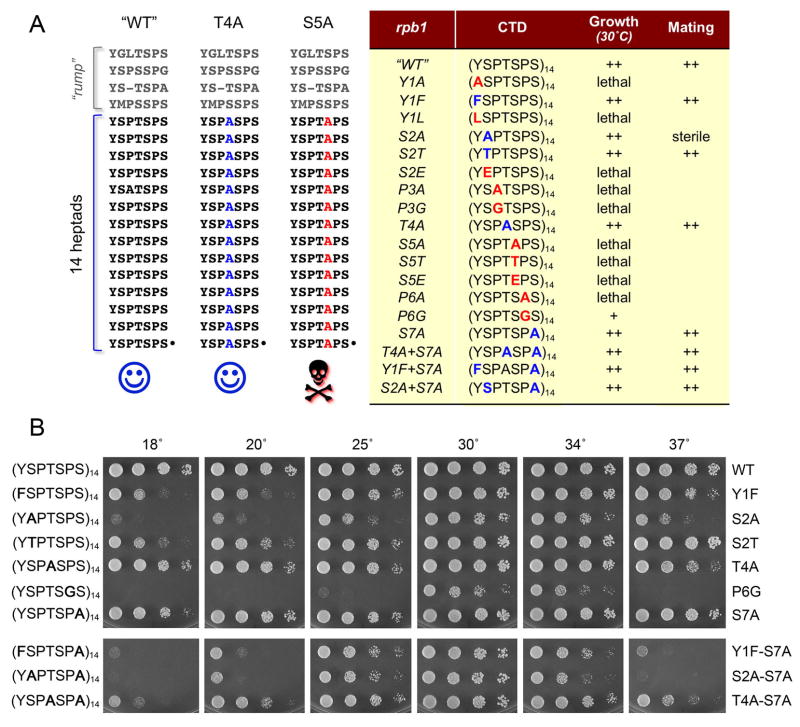
Figure 1. Effects of CTD mutations on fission yeast viability, vegetative growth, and mating proficiency.
(A) The amino acid sequences the CTDs encoded by rpb1 alleles “WT”, T4A and S5A are displayed at left with the heptad repeats aligned vertically. The alleles are named according to the amino acid substitutions introduced into all 14 consensus heptads appended to the “rump” that connects the CTD to the body of Pol II. A summary of the mutational effects on growth and mating is compiled in the Table at right. (B) Viable S. pombe strains with the indicated rpb1-CTD alleles were grown in liquid medium until A600 reached 0.6 to 0.9. The cultures were adjusted to A600 of 0.1 and aliquots (3 μl) of serial 5-fold dilutions were spotted on YES agar plates. The plates were photographed after incubation for 8 d at 18°C, 6 d at 20°C, 3 d at 25° or 2.5 d at 30°, 34° and 37°C.