Table 3.
Oxidation of simple bis(indoles) with peptide 22 as a catalyst.
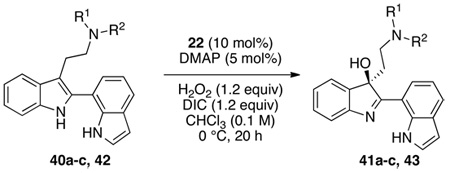 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| entry | bis-indole | hydroxy-indoleninea | R1 | R2 | yield (%) | er |
| 1 | 40a | 41a | 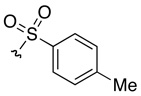 |
H | 77 | 86:14 |
| 2 | 40b | 41b | 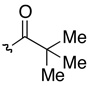 |
H | 87 | 83:17 |
| 3 | 40c | 41c | 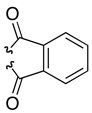 |
89 | 82:18 (95:5)b | |
| 4 | 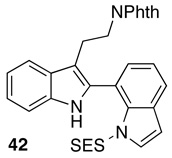 |
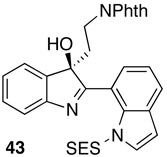 |
70 | 93:7 | ||
Reaction conditions for indole oxidation: indole (1.0 equiv), peptide (10 mol%), and DMAP (5 mol%) in CHCl3 (0.1 M) at 0 °C, then add aq. H2O2 (1.2 equiv), and DIC (1.2 equiv).
Recrystallized to 95:5 er from 95/5 2-propanol/ethanol mixture (yield after recrystallization 47%).
DMAP = N,N-dimethyl-4-aminopyridine, DIC = diisopropylcarbodiimide, Phth = phthaloyl, SES = 2-(trimethylsilyl)ethylsulfonyl.
