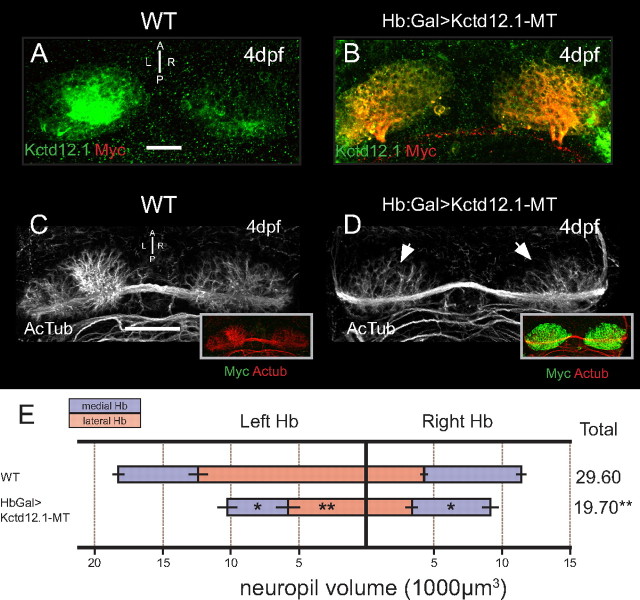
Figure 5.
Overexpression of Kctd12.1 inhibits elaboration of Hb neuropil. A, Kctd12.1 (green) is normally expressed only in Hb neurons of the lateral subnuclei. B, In Hb:Gal>Kctd12.1-MT larvae, Kctd12.1-MT fusion protein (red) is expressed at high levels in nearly all Hb neurons. C, D, WT larvae have an elaborate network of neuropil that segregates within each Hb subnucleus (C), but the presence of high levels of ectopic Kctd12.1-MT fusion inhibits the elaboration of Hb neuropil (D). E, Volumetric quantification of Hb neuropil reduction. Overexpression of Kctd12.1-MT causes significant reduction of total Hb neuropil volume compared with WT (19,693 ± 1664 vs 29,602 ± 1426 μm3; p = 0.002; n = 16). All subnuclei are significantly affected with the exception of the right lateral subnucleus (asterisks indicate statistical difference compared with WT). Scale bars, 50 μm. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, two-tailed t test.