Fig. 1.
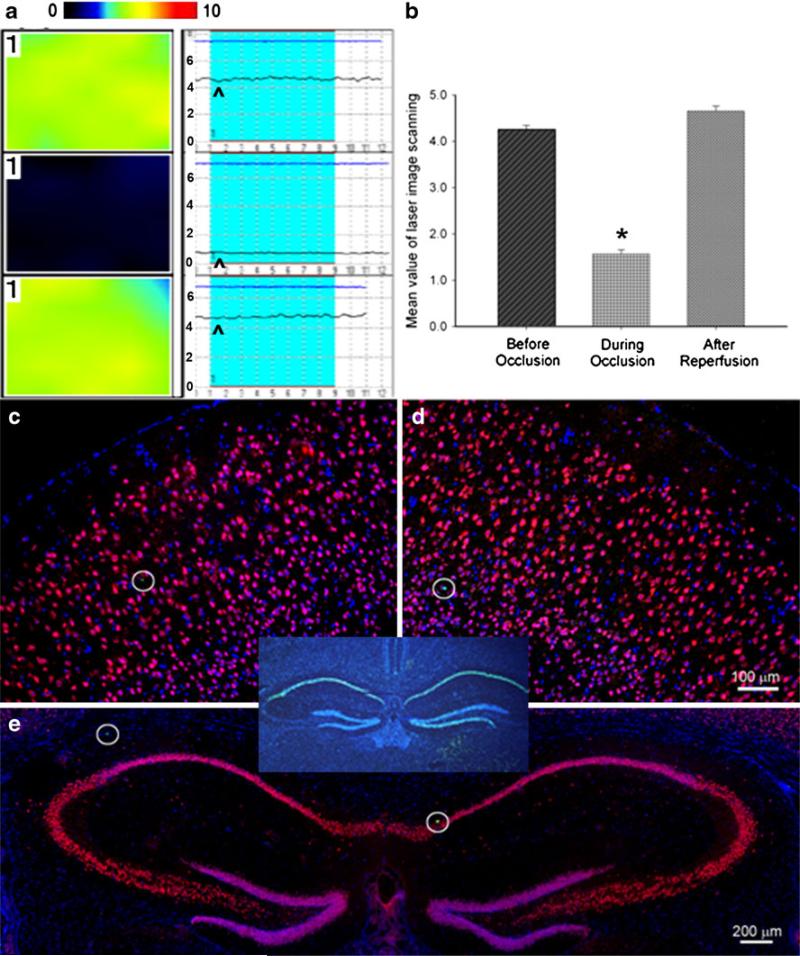
Sublethal global ischemia reduced CBF but did not induce cell death. a The laser Doppler scanning images (left column) and laser Doppler probe single point measurement (right column) show CBF before (top), 1 min after (middle) CCA occlusion, and right after reperfusion (bottom) in the right hemisphere. The color in the laser scanning image represents the level of the blood flow; color standard bar is shown on the tope where the blood flow level (black to red) stands for 0 to 10 (maximal). In the laser Doppler single point panel, the arrowhead points to the line representing the level of CBF. b Average of mean image values in laser scanning imaging at different time points. Cerebral blood flow showed 65% reduction after CCA and restored after reperfusion. *P<0.01. N=6 in each group. c–e TUNEL (green), NeuN (red), and Hoechst 33342 (blue) staining 7 days after transient global ischemia showed that there was no delayed neuronal death in either side of the neocortex and hippocampus (e). The hollow circles showed TUNEL-positive cells (green) which indicated the natural cell death in the brain. The insert provides a positive control of TUNEL staining, showing massive cell death (green) in the hippocampus after an 11-min TGI in C57BL/6 mouse. Bar=100 μm in c and d. Bar=200 μm in e