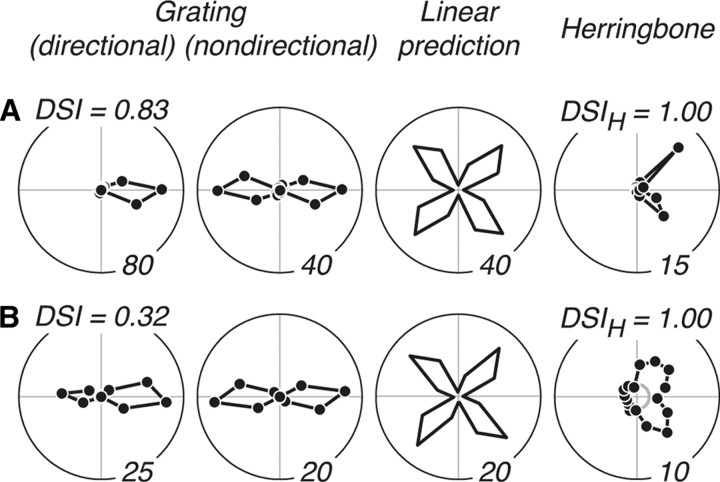
Figure 8.
Direction selectivity for gratings and herringbones. A, B, Data for two example V2 neurons with directional herringbone responses, where only two adjacent tuning lobes were evident. For each, we show the tuning for grating direction (column 1) from which we generated the nondirectional grating tuning curve (column 2) that formed the basis of our linear response prediction (column 3). We also show the measured tuning for herringbone direction (column 4). A, Responses of a neuron that was strongly direction selective for gratings, with a high direction selectivity index (DSI = 0.83). It was also strongly direction selective for herringbones, with a high herringbone direction selectivity index (DSIH = 1) (see text). B, Responses of a neuron that was weakly direction selective to gratings (DSI = 0.32) but was nevertheless strongly direction selective to herringbones (DSIH = 1).