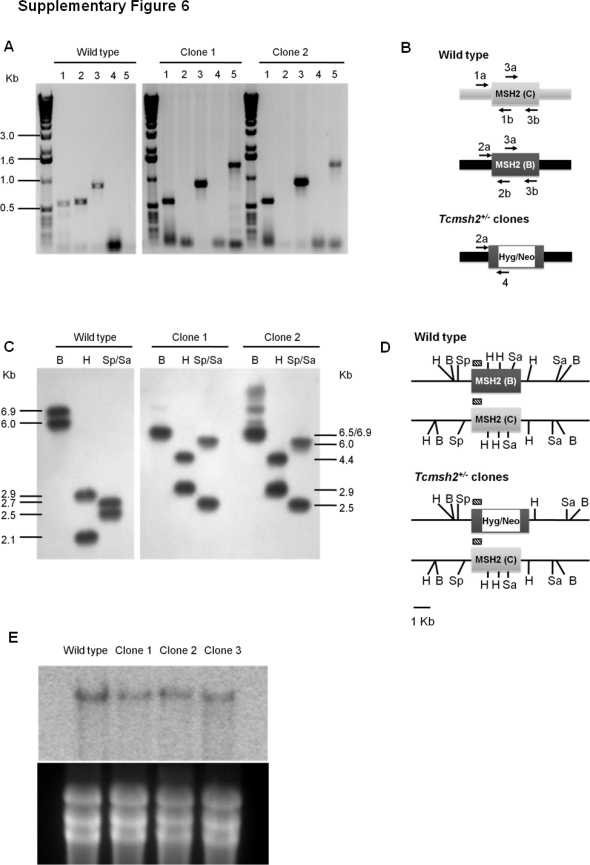
Supplementary Fig. 6.
Characterization of T. cruzi ΔTcmsh2::HYG/TcMSH2 clones. A: agarose gel electrophoresis of PCR products obtained with, lane 1: allele C-specific primers (1a and 1b); lane 2: allele B-specific primers (2a and 2b); lane 3: Tcmsh2 internal common primers (3a and 3b); lane 4: allele C-specific forward primer and resistance gene-specific reverse primer (1a and 4); lane 5: allele B-specific forward primer and resistance gene-specific reverse primer (2a and 4). In B is shown a schematic diagram of the TcMSH2 locus in the CL Brener strain genome (wild type and ΔTcmsh2::HYG/TcMSH2 clones) and annealing sites of all primers used in A. In C is shown a Southern blot of T. cruzi genomic DNA from epimastigote cultures of the CL Brener wild type and ΔTcmsh2::HYG/TcMSH2 clones. Parasite DNA was digested with BamHI, HindIII and SphI/SalI, hybridized with the indicated labelling probe and exposed to a X-Ray film. The sizes of probed fragments are indicated. The probe used in Southern and Northern blots is represented by hachured lines and the restriction sites for BamHI (B), HindIII (H), SphI (Sp) and SalI (Sa) are indicated in D. In E is shown the expression of the TcMSH2 transcripts. Northern blot analyses were performed with total RNA extracted from epimastigotes of CL Brener wild type and ΔTcmsh2::HYG/TcMSH2 clones. Messenger RNA samples were hybridized with a radiolabed probe indicated in D. The bottom part of the figure shows ethidium bromide staining of rRNA bands to indicate the amount of mRNA loaded on the gel.