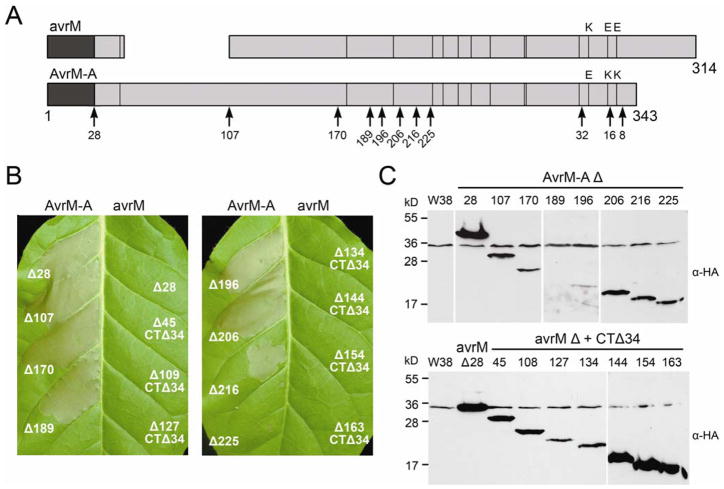
Fig. 2.
C-terminal domain of AvrM elicits M-dependent cell death. A, Schematic diagram showing variation between AvrM-A and avrM proteins with the size of each protein as amino acid length shown at the end. The signal peptide is shaded dark and lines indicate positions of polymorphic residues; the last three variable residues are given. The position of the N-terminal 69-amino-acid (aa) deletion and the 34-aa extension of avrM are shown. N- and C-terminal truncation sites are indicated by arrows along with the amino acid number, and the size of each full-length protein in amino acids is given. B, Leaves of transgenic W38 tobacco carrying the M gene were infiltrated with Agrobacterium cultures containing T-DNA plasmids encoding AvrM-A (left side of leaf) and avrM (right side of leaf) truncations with an N-terminal hemagglutinin (HA) epitope tag. The size of the N-terminal truncation (Δ) is given and CTΔ34 indicates that the avrM truncations were made with the 34-aa C-terminal extension removed. Leaves were photographed 3 days after infiltration. C, Protein extracts from tobacco leaf tissue (W38) and leaf tissue transiently expressing HA–AvrM-A (upper) or HA–avrM (lower) truncations were analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-HA (α-HA). Positions and sizes of protein molecular mass standards are indicated.