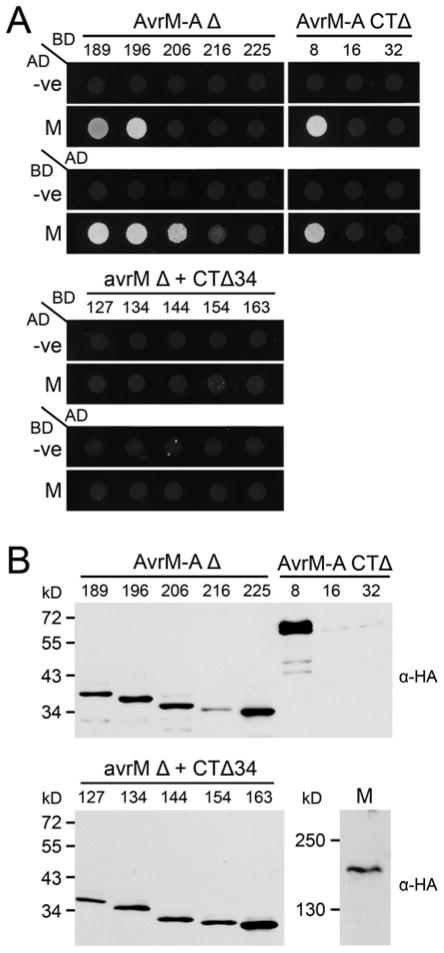
Fig. 4.
Interactions of AvrM-A truncations with M protein in yeast. A, Growth of yeast strain AH109 expressing GAL4-activation domain (AD) and -binding domain (BD) fusion proteins on minimal media lacking histidine. Upper panel: strains expressing BD–AvrM-A N-terminal (Δ; left) and C-terminal (CTΔ; right) truncations with AD alone (-ve) or AD–M fusion protein. Strains expressing the reversed fusions are shown below; AD–AvrM-A truncations with BD–green fluorescent protein (-ve) or BD–M. Lower panel: strains expressing the corresponding BD–avrM truncated proteins (N-terminal [Δ] plus C-terminal [CTΔ34] to remove an additional 34-amino-acid extension) with AD alone (-ve) or AD–M. Strains expressing the reversed fusions are shown below; AD–avrM truncations with BD alone (-ve) or BD–M. B, Protein extracts from yeast strain AH109 expressing AD–AvrM-A (upper), AD–avrM, or AD–M (lower) fusion proteins were analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-hemagglutinin (α-HA). Positions and sizes of protein molecular mass standards are indicated.