Fig. 3.
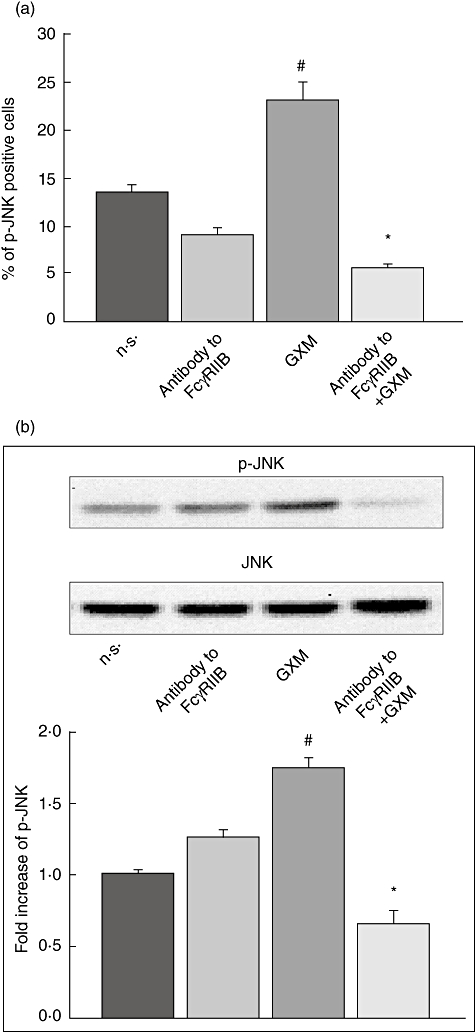
Role of FcγRIIB in glucuronoxylomamman (GXM)-induced c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase (JNK) activation. MonoMac6 cells (1 × 106/ml), treated as described in Fig. 1, were stained with antibodies to p-JNK and analysed by flow cytometry or Western blotting. (a) Percentage of p-JNK-positive cells. Bars represent the mean ± standard error of the mean (s.e.m.) of three experiments. (b) Western blotting for p-JNK. JNK was used as loading control. Optical density (OD) of reactive bands was measured and normalized by the JNK intensity in the same lane. Blot is representative of results obtained from five separate experiments. The fold increase is the mean ± s.e.m. of five experiments. (a,b) The incubation with irrelevant goat polyclonal immunoglobulin (Ig)G did not affect JNK activation. #P < 0·05 (GXM-treated versus untreated); *P < 0·05 (antibody to FcγRIIB plus GXM-treated, versus GXM-treated).
