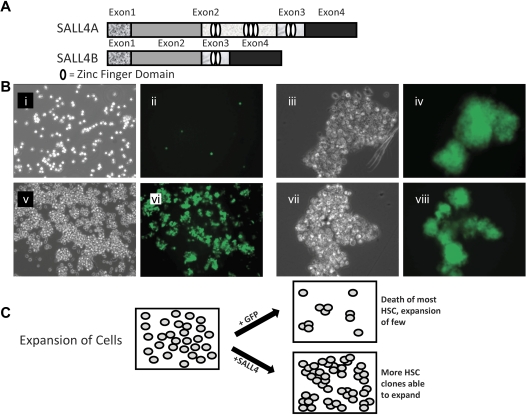
Figure 1.
SALL4 isoforms and SALL4-transduced HSC expansion. (A) Schematic diagram of the SALL4A and SALL4B isoforms demonstrating the variable number of zinc-finger domains possessed by each. The HSCs were transduced with either the SALL4A or SALL4B gene using a lentiviral transfection system. (B) Bright field and fluorescent images of human bone marrow CD34+ cells transduced with GFP (i-ii, 10×) or representative SALL4 isoform B (v-vi, 10×) 9 days after infection. Initially, 50 000 CD34+/CD38− cells were plated. High magnification of SALL4B-transduced HSC clusters (iii,iv,vii,viii, 40×). The GFP cell clusters signified positive overexpression of SALL4B. With SALL4B overexpression, HSC cell clusters are able to survive and are rapidly expanding at 9 days after infection. (C) Model of SALL4-mediated ex vivo HSC expansion. The primary culture was divided and transduced with a SALL4 or GFP control. The viable HSCs without SALL4 overexpression decreased in number because of differentiation or death leading to a net HSC decline. In contrast, HSCs in which SALL4 was overexpressed, many clones were able to survive and expand in the culture. A net HSC expansion was exhibited with numerous expanding clusters throughout the culture.