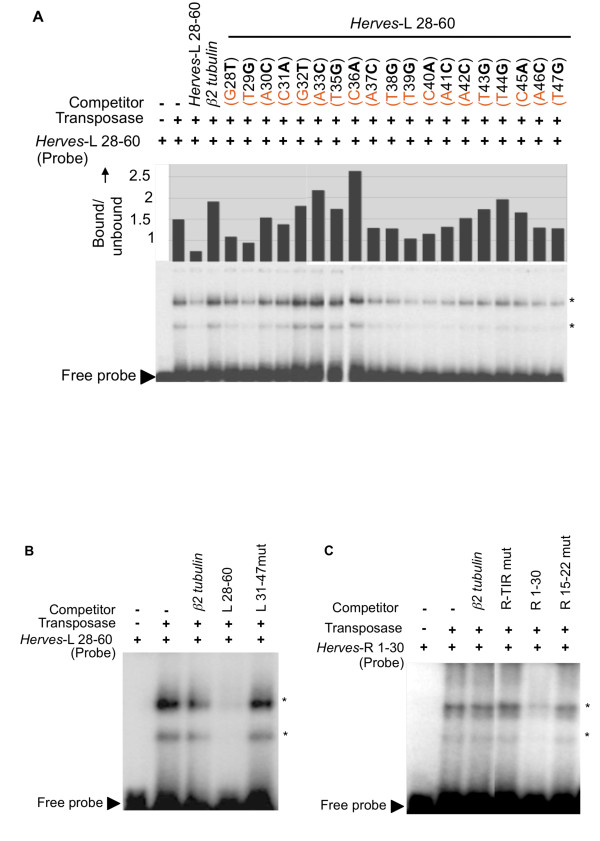
Figure 5.
CGATTCAT acts as transposase binding motif. (a) Electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA) analysis of transposase binding to the Herves-left (L) bp 28-60 probe and single nucleotide sequence variants as competitors. For example: G28T indicates that G at position 28 was changed to T in the Herves-L bp 28-60 fragment. The fraction of the transposase bound probe in each lane was quantified using a phosphoimager. Mutations that have no effect on the transposase binding are expected to produce values similar to the specific competitor. (b) The Herves-L 31-47 region is important for binding. The asterisk (*) indicates various protein DNA complexes. The Herves-L 28-60 bp fragment was used as a probe in EMSA experiment. The Herves-L 31-47mut carries mutations at every position within bp 31-47. (c) Role of right (R)-terminal inverted repeat (TIR) in the transposase binding. The Herves-R bp 1-30 fragment was used as a probe. The Herves-R TIRmut and R 15-22mut fragments consist of the Herves-R bp 1-30 sequence with mutations in TIR and bp 15-22 respectively. The probe was incubated in the presence (+) or absence (-) of the transposase or competitors. Unlabeled homologous and non-homologous fragments were used as specific and non-specific competitors, respectively. The asterisk (*) indicates various protein DNA complexes.