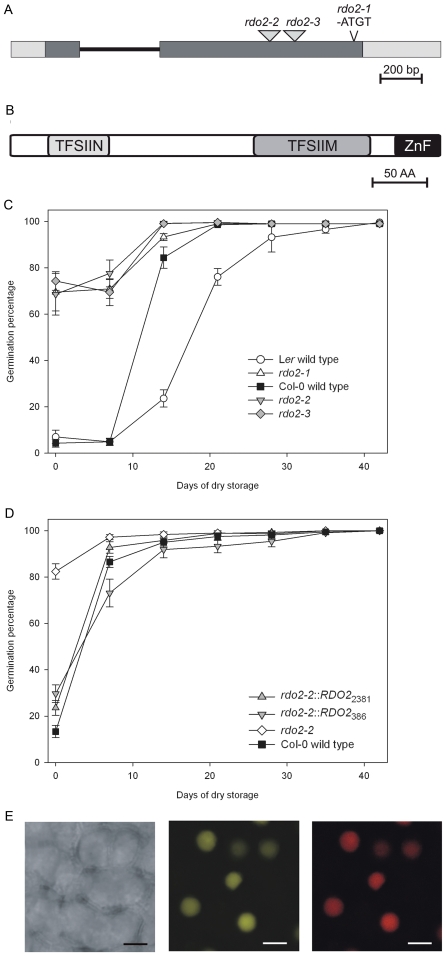
Figure 1. Characterisation of RDO2.
(A) Schematic representation of the RDO2 gene, indicating the positions of the rdo2-1 4 bp deletion and the rdo2-2 and rdo2-3 T-DNA insertions. Exons in the RDO2 locus are represented as grey boxes, UTR regions as white boxes and the intron as a black line. (B) Schematic representation of RDO2 structural protein domains; Transcription factor IIS, N-terminal (TFSIIN), Transcription elongation factor S-IIM (TFSIIM) and Zinc finger (ZnF), obtained by At2g38560 protein analysis with the Simple Modular Architecture Research Tool (SMART) [49]. (C) Dormancy/germination behaviour of rdo2-1 (white triangles up) and wild-type Ler (white circles), rdo2-2 (SALK_027259; grey triangles down), rdo2-3 (SALK_133631; grey diamond) and wild-type Col (black squares). Germination is expressed as percentage of germinated seeds after different periods of seed dry storage starting from harvest. Error bars represent SE, n≥14. (D) Dormancy/germination behaviour of complemented rdo2-2 mutants. The rdo2-2 mutant (SALK_027259; white circles) was complemented with genomic-DNA fragments containing the complete RDO2 coding sequence and 386 bp (rdo2-2::RDO2386; grey triangles down) or 2381 bp (rdo2-2::RDO22381; grey triangles up) upstream of the RDO2 start codon. Col wild-type is shown as black squares. Germination is expressed as percentage of germinated seeds after different times of seed dry storage starting from harvest. Error bars represent SE, n≥14. (E) YFP signal in nuclei of rdo2 mutant plants that were stably transformed with a p2X35S:RDO2:YFP construct. Left panel transmission, middle panel YFP fluorescence, right panel Propidium Iodide staining. Scale bar represents 3 µm.