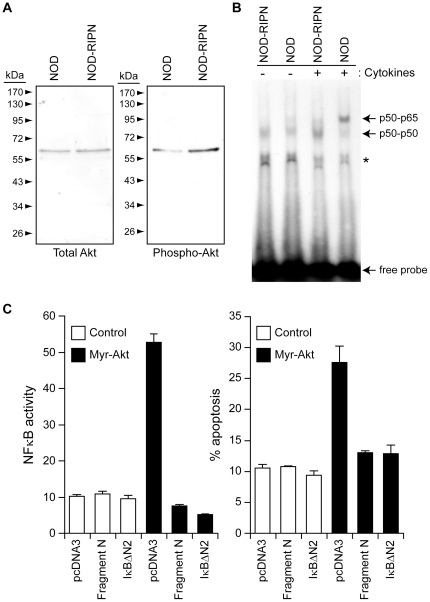
Figure 2. Signals modulated by fragment N.
A. The extent of Akt activation was assessed by Western blot analysis of 10 µg of lysates from islets isolated from 5 week-old female mice using an antibody recognizing the phosphorylated form of Akt. Total levels of Akt were also determined using a non-phospho-specific anti-Akt antibody. B. Islets isolated from NOD and NOD-RIPN mice were stimulated or not for 30 minutes with inflammatory cytokines (1,000 units/ml tumor necrosis factor-α, 1,000 units/ml interleukin-1β, and 50 units/ml interferon-γ). The ability of nuclear proteins to interact with an NFκB-binding element-bearing radioactive probe was then monitored by EMSA as described in the methods. The locations of p65-p50 and p50-p50 complexes are indicated. The asterisk denotes a nonspecific band. C. INS1 cells were transfected with an empty vector (pcDNA3), a plasmid encoding the myristoylated active form of Akt (myr-Akt), a plasmid encoding a super NFκB repressor (IkBαΔN2), or a plasmid encoding fragment N in the indicated combinations, together with a NFκB-reporter luciferase construct and a GFP-encoding plasmid (to label the transfected cells). One day after, transfection, the cells were lysed to assess NFκB activity (left panel). Alternatively, apoptosis was scored in the transfected cells (right panel).