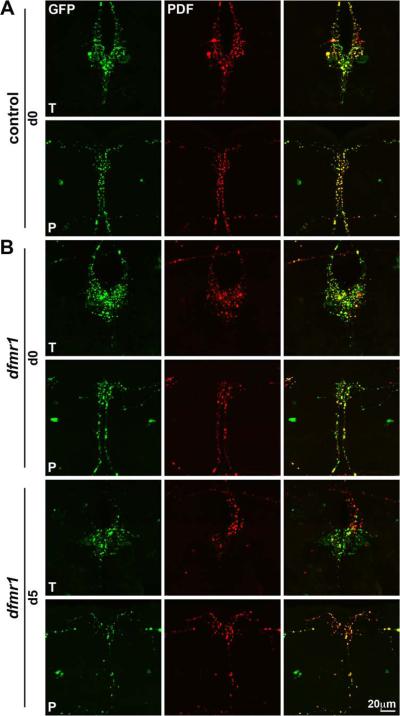
Figure 5. Null dfmr1 PDF-TRI neurons maintain synaptic architecture.
Representative images of Pdf-Gal4 driven synaptic marker UAS-synaptotagmin-GFP in PDF-TRI neurons (GFP, green) double-labeled for the PDF neuropeptide (red). As oriented in Supplemental Fig. 1, trito- (T) and protocerebral (P) regions are shown. A) Control brains immediately after eclosion (day 0; d0) show developmentally-transient PDF-TRI neurons with an extensive array of differentiated synaptic boutons. B) Null dfmr150M mutants at d0 (top) and d5 (bottom). Similar synaptic arrays are present in control and mutant at the early time point, immediately following eclosion. PDF-TRI synaptic boutons are maintained at maturity (d5) only in the dfmr1 null brain, with an extensive array of remodeled synaptic boutons in both trito- (T) and protocerebral (P) brain regions.