Figure 1.
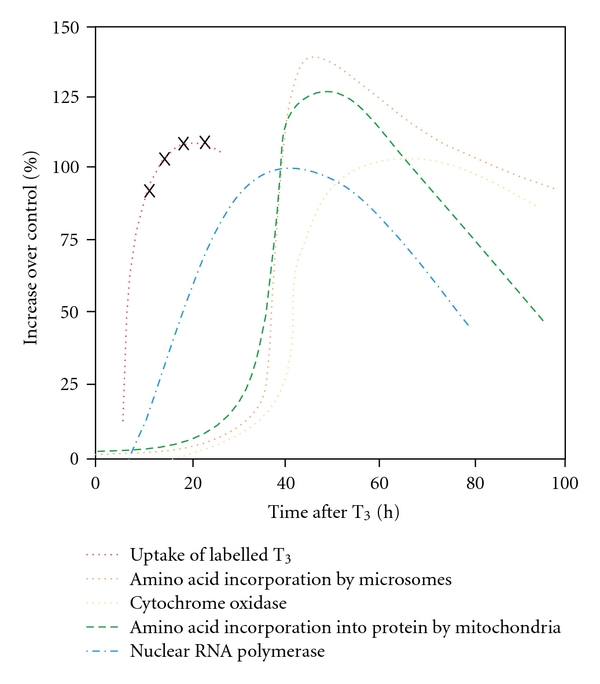
An idealized representation of the time course of response of some activities of nuclei, mitochondria, and microsomes from livers of thyroidectomized rats after a single injection of 20 μg T3/100 g. body wt. The stimulatory effects are expressed as % increase in specific activity in the different subcellular fractions from T3-injected animals over control animals. The main features are the following: (a) mitochondrial respiration (here expressed as cytochrome oxidase activity) reached a peak after amino acid incorporation into protein by microsomes and mitochondria; (b) the increase in protein synthetic capacity of the two organelles was coupled, following a relatively long lag period after hormone administration; (c) nuclear RNA polymerase activity was enhanced several hours before cytoplasmic protein synthesis and BMR. The time course of nuclear accumulation of T3 (×⋯×; [18]) is superimposed on that of the hormonal effects on mitochondrial, transcriptional, and protein synthetic activities (Data assembled from [22–24]).
