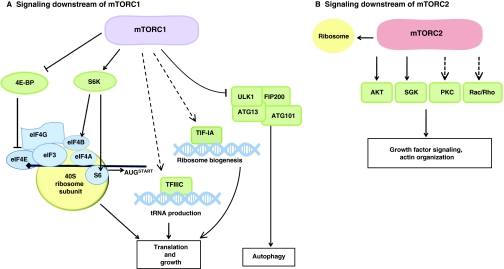
Fig. 4.
Downstream effectors of mTORC signaling. (A) Mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1) phosphorylation of eukaryotic initiation factor 4E (eIF4E)-binding protein (4E-BP) disrupts the interaction of 4E-BP with eIF4E, which leaves eIF4A free to promote the binding of ribosomes to the transcriptional start site. mTORC1 also activates ribosomal S6 kinase (S6K), which activates the translational initiation factor eIF4B and the S6 ribosomal protein by direct phosphorylation. mTOR can also associate with general transcription factor III C (TFIIIC) and relieve its inhibitor Maf1, leading to increased tRNA production. TORC1 activity also promotes association between transcription initiation factor 1A (TIF-1A) and polymerase I (PolI), thereby promoting rRNA synthesis. Finally, mTORC1 signaling can inhibit autophagy through phosphorylation of Unc-51-like kinase 1 (ULK1) and autophagy related 13 homolog (ATG13). (B) mTORC2 phosphorylates and activates AKT (a serine/threonine protein kinase) and serum/glucocorticoid regulated kinase (SGK), and has been implicated in signaling via protein kinase C (PKC) and Rac/Rho. Collectively, these mTORC2-mediated activities promote growth factor signaling and cytoskeletal reorganization. In response to insulin signaling, mTORC2 can also interact with ribosomes. Abbreviation: ATG101, autophagy-related protein 101; FIP200, FAK family interacting protein of 200 kDa.