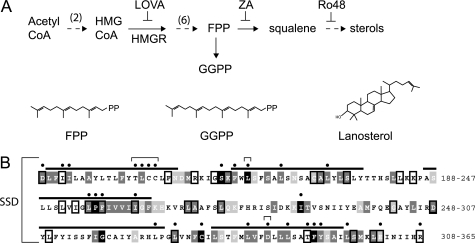
FIGURE 1.
A, abbreviated sterol synthesis pathway. Inhibitors that increase (ZA) or decrease (Lova) the FPP-derived degradation signal for Hmg2 are indicated. Lova inhibits HMGR, and ZA inhibits squalene synthase. Ro48 inhibits oxidosqualene epoxidase, inducing an alternative oxysterol-producing pathway (23) Structures of the 15-carbon FPP and 20-carbon GGPP isoprenes and lanosterol are depicted. B, the Hmg2 SSD conservation and mutants. Membrane spans are over-lined. The extent of conservation for each residue in five different SSDs (alignments shown in supplemental Fig. S1) is indicated by color: black for identical residues, dark gray for conservation, and light gray for semi-conservation. Boxes represent identity in four of five different SSD sequences examined. Alignments and conservation were determined by the T-Coffee multiple sequence alignment program. Hmg2 (YLR450W ORF) protein sequence is from the Saccharomyces Genome Database. Thirty mutants were made in this study. Black dots mark mutated residues; brackets mark residues in Hmg2 that correspond to sterol-insensitive mutants in HMGR and SCAP, e.g., the YIYF to AAAA mutant, Tyr-298, Leu-315, and Asp-428.