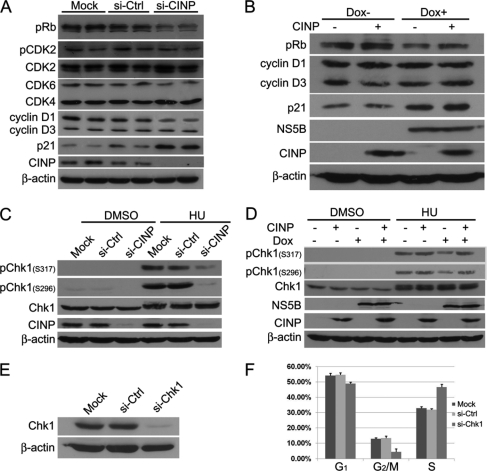
FIGURE 8.
NS5B modifies DNA damage response. A, HepG2 Tet-On NS5B stable cells were transfected with CINP-specific or control siRNA (si-Ctrl) without Dox addition. Seventy-two hours later, the cells were harvested, and Western blot analysis was performed with the indicated antibodies. siCINP and siGFP transfections were performed in duplicate in each experiment. B, HepG2 Tet-On NS5B stable cells with or without Dox were transfected with or without CINP-expressing plasmids. Forty-eight hours later, the cells were harvested, and Western blot analysis was performed. C, HepG2 Tet-On NS5B stable cells were transfected with CINP-specific or control siRNA without Dox. Forty-eight hours later, the cells were treated with 3 mm hydroxyurea (HU) or an equal volume of DMSO. After incubation for another 24 h, the cells were harvested for Western blot analysis with anti-pChk1 (Ser-296 and Ser-317) and anti-Chk1 antibodies. D, HepG2 Tet-On NS5B stable cells with or without Dox were transfected with or without CINP-expressing plasmids. Twenty-four hours later, the cells were treated with 3 mm hydroxyurea or an equal volume of DMSO. After incubation for another 24 h, the cells were harvested for Western blot with anti-pChk1 (Ser-296 and Ser-317) and anti-Chk1 antibodies. E, HepG2 Tet-On cells were transfected with 60 nm Chk1-specific siRNA or control siGFP. Seventy-two hours later, the knockdown efficiency was detected by an anti-Chk1 antibody. F, after transfection with Chk1-specific siRNA for 72 h, HepG2 Tet-On cells were analyzed for DNA content by flow cytometry. The results are representative of three independent experiments. Error bars indicate S.D.