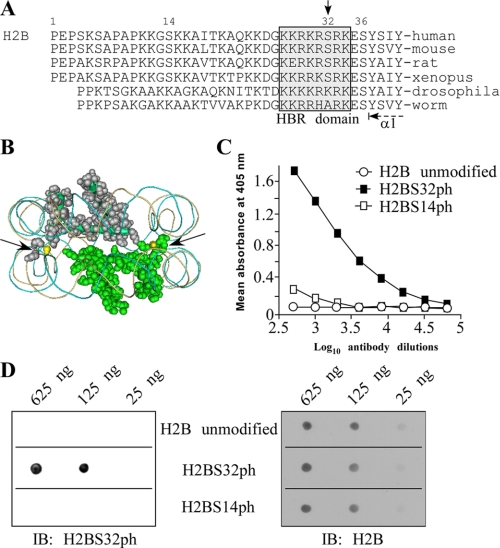
FIGURE 1.
Confirmation of antibody to specifically detect H2BS32ph. A, comparison of the primary sequences of histone H2B N-terminal “tails” from different species shows that only vertebrates have a well conserved Ser32 or Ser14, whereas a highly conserved Ser36 is evident in the H2B tails of most species from human to worm. Ser32 (downward arrow) is the only serine located within the HBR domain (gray box). B, location of Ser32 residues (yellow) in the nucleosome crystal structure (Protein Data Bank code 2CV5). Shown are two molecules of H2B present in the nucleosome (image drawn using Cn3D version 4.1). The arrows indicate the location of the pair of H2BS32 residues, each at the extreme end of the N-terminal tail of H2B and in between the DNA grooves. C, peptide competition analyses confirm the specificity of the H2BS32ph antibody. The specificity of the antibody was validated by peptide competition using ELISA. The antibody, which was raised against an H2BS32ph peptide, specifically recognizes only this peptide and fails to detect the identical but unmodified H2B peptide. Similarly, the antibody does not recognize other phosphoserine sites like H2BS14 previously shown to be modified on H2B. D, the indicated amounts of various phosphorylated histone peptides were spotted onto a PVDF membrane and probed with the H2BS32ph antibody. This antibody only recognizes the peptide containing phosphorylated Ser32 (left panel). The same blot was stripped and reprobed with the H2B antibody as a loading control (right panel). IB, immunoblot.