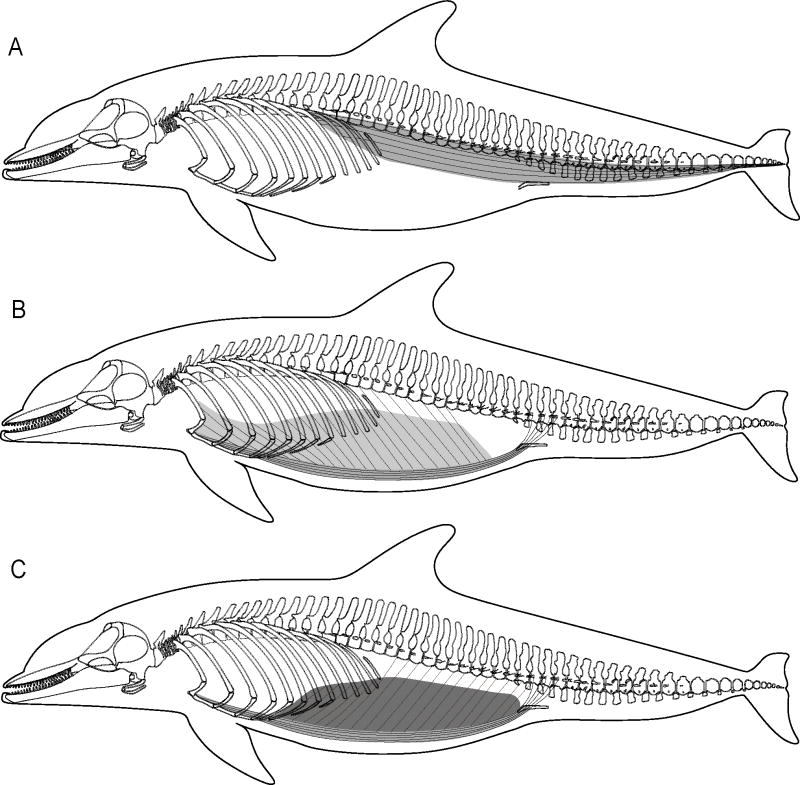
Fig. 8.
Lateral view of the (A) hypaxialis, (B) external abdominal obliques and rectus abdominis, and (C) internal abdominal obliques and rectus abdominis in bottlenose dolphins (Tursiops truncatus). Thin black lines represent the tendons of origin of the abdominal oblique muscles and the tendons of the rectus abdominis that insert onto caudal vertebrae.