Figure 3.
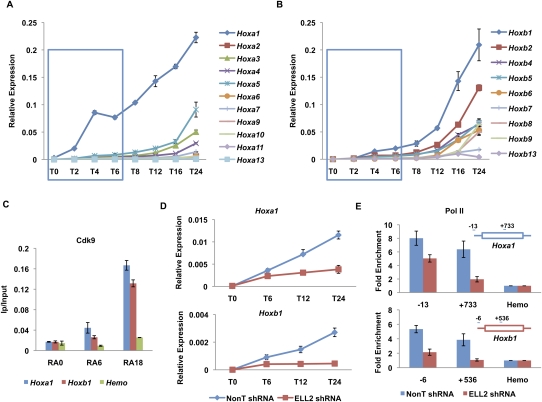
SEC is required for the rapid induction of the Hoxa1 gene. (A,B) RT-qPCR analysis of Hoxa and Hoxb cluster genes upon RA treatment. ES cells were treated with RA for different time points as indicated. Total RNAs were extracted from these cells and then subjected to RT-qPCR analysis using an Applied Biosystems' custom TaqMan array card. Hoxa1 was the first Hox gene to be induced by RA. Compared with Hoxa1, the induction of Hoxb1 was much slower within the first 6 h of RA treatment. The blue boxes indicate the first three RA induction time points. (C) Cdk9 is recruited to both the Hoxa1 and Hoxb1 gene promoters. Cdk9 ChIP was performed to measure its enrichment on Hoxa1 and Hoxb1 after RA treatment. A hemoglobin gene, Hba (Hemo), serves as a nontranscribed control gene. (D) ELL2 RNAi inhibits the induction of Hoxa1 and Hoxb1 by RA. shRNA targeting ELL2 or nontargeting shRNA (NonT) was introduced by lentiviral infection for 3 d before RA treatment. (E) Knockdown of ELL2 reduces Pol II occupancy at Hoxa1 and Hoxb1 after 6 h of RA treatment. Pol II occupancy was assayed by ChIP at the start site of transcription and in the ORF of Hoxa1 and Hoxb1 in RA-induced cells. Pol II is reduced in the ORF of both Hoxa1 and Hoxb1, and Hoxb1 also shows dramatically reduced levels of Pol II at its promoter after ELL2 RNAi. The Hoxa1 promoter, but not the Hoxb1 promoter, has prebound Pol II before RA treatment (see Fig. 2; Supplemental Fig. S4). Error bars represent the standard deviation.