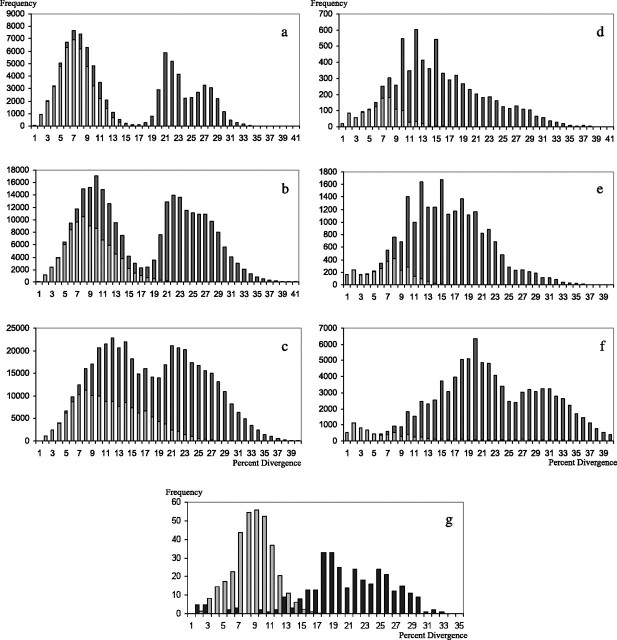
FIG. 4.
Frequency histogram of pairwise distances found in intra (light shading) and inter (dark shading) group comparisons. The four sequence groups used for primates are (a) human DRB1, DRBX (which is DRB3, 4, or 5), DPB1, and DQB1 (b) Catarrhine DRB1, DRBX (consisting of nonspecified DRB duplicate loci), DPB1, and DQB1 (c) Strepsirrhine and haplorrhine DRB1, DRBX, DPB1, and DQB1. A variable number of sequence groups is used for birds. The groups are (d) 9 groups including all assigned DFs; (e) the same 9 groups including all DFs and CFs assigned to those groups; (f) all 15 groups including all the assigned DFs and CFs. The horizontal axis indicates the number of substitutions per 100 sites (estimated using Kimura’s two-parameter method) found in pairwise sequence comparisons, whereas the ordinate indicates the frequency of occurrence of a specific number of substitutions. (g) The distribution found for available fowl (light shading, 104 unique sequences) and quail (dark shading 39 unique sequences) MHC class II B sequences. The frequency values in pairwise comparisons of fowl sequences are shown at 10% of the true height to make them comparable with that of the quail.