Figure 1.
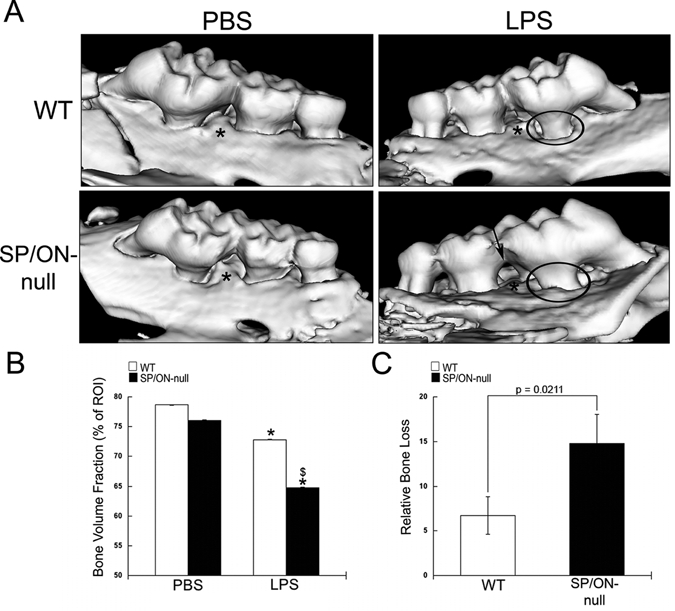
SP/ON-null maxillae injected with LPS demonstrated significantly decreased alveolar bone volume fraction (BVF) in comparison with WT maxillae. (A) Representative µCT reconstructions for WT and SP/ON-null maxillae injected with PBS and LPS. LPS injections caused significant bone resorption in both WT and SP/ON-null mice. In (A), * indicates the injection sites, circles indicate areas of bone loss with increased root structure visible above the alveolar bone crest, and arrow indicates extensive bone loss in the interproximal aspects of SP/ON-null LPS-injected mice. (B) Quantification of BVF reveals statistically significant decreases in bone volume associated with LPS injections in both WT (white bars) and SP/ON-null (black bars) mice in comparison with their respective PBS controls. * indicates p < 0.05 from PBS control. $ indicates p < 0.05 statistical significance of WT LPS vs. SP/ON-null LPS-injected mice. Error bars = standard deviation. (C) Comparison of relative bone loss indicates that bone loss caused by LPS injections in SP/ON-null mice was significantly greater than that in WT mice. P-value determined by Student’s t test. Error bars = SEM.
