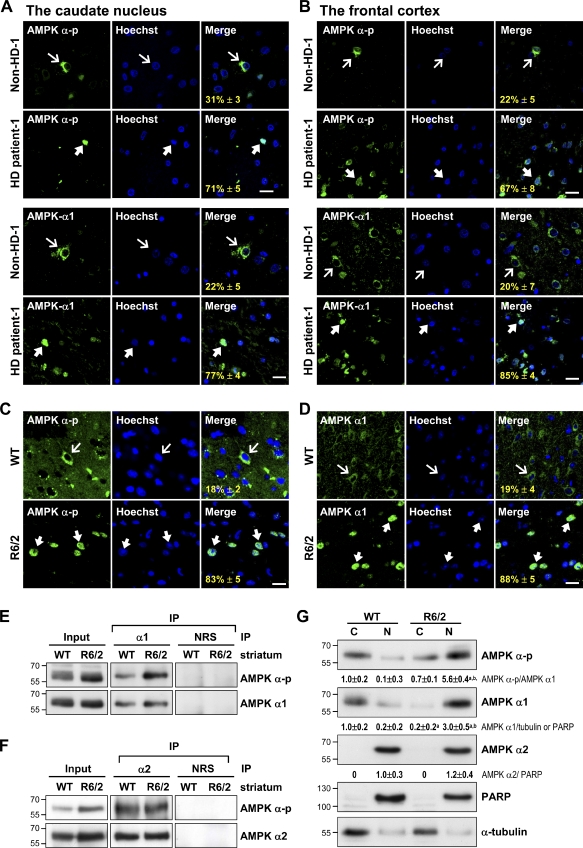
Figure 1.
Selective activation and nuclear enrichment of AMPK-α1 in striatal neurons of patients and mice with HD. (A and B) The caudate nucleus (A) and frontal cortex (B) of HD patients and age-matched controls were analyzed. Immunofluorescence staining of AMPK-α-p (green) or AMPK-α1 (green) was conducted. (C and D) Immunofluorescence staining of AMPK-α-p (C, green) or AMPK-α1 (D, green) was conducted in brains of 12-wk-old mice. Nuclei were stained with Hoechst (blue). The numbers shown in the bottom left corners of the merged images are the percentages of cells expressing nuclear AMPK-α-p or AMPK-α1. Thin arrows mark cells containing AMPK, which are located mostly in cytoplasmic regions. Thick arrows mark cells with nuclei enriched with AMPK. Values represent the mean ± SEM of at least three independent experiments. At least 200 cells from each sample were analyzed. Bars, 20 µm. (E and F) Total striatal lysate of 12-wk-old mice was immunoprecipitated (IP) using the indicated antibody and subjected to Western blot analyses. (G) The cytoplasmic (C) and nuclear (N) fractions were harvested from the striatum of 12-wk-old mice and assessed using Western blot analysis. PARP and α-tubulin were respective markers for the nuclear and cytoplasmic fractions. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. Molecular mass is indicated in kilodaltons. a, P < 0.05 versus WT cytoplasmic; b, P < 0.05 versus WT nuclear. NRS, normal rabbit serum.