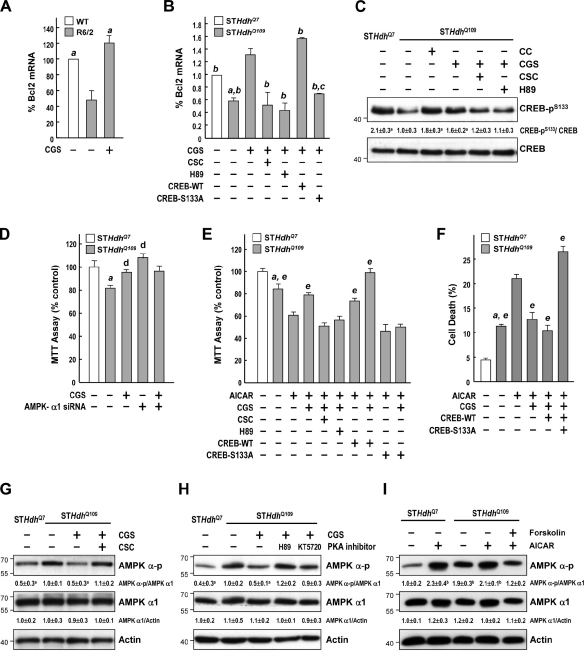
Figure 9.
Stimulation of the A2AR rescued AMPK-mediated suppression of Bcl2 via a PKA–CREB-dependent pathway. (A) Mice were treated daily with CGS (2.5 mg/kg of body weight, i.p.) or vehicle for 6 wk from the age of 4 wk. Transcript levels of Bcl2 assessed by reverse transcription qPCR were normalized to those of GAPDH. a, P < 0.05 versus R6/2 mice. (B and D–F) Cells were transfected with the indicated constructs for ∼24–48 h and then treated with the indicated reagents for 24 h. Transcript levels of Bcl2 assessed by reverse transcription qPCR were normalized to those of GAPDH (B). a, P < 0.05 versus untreated STHdhQ7 cells; b, P < 0.05 versus STHdhQ109 cells treated with CGS; c, P < 0.05 with a specific comparison between cells transfected with CREB-WT and CREB-T133A; d, P < 0.05 versus untreated STHdhQ109 cells; e, P < 0.05 versus AICAR-treated cells. (D–F) Cell survival was determined using an MTT assay (D and E) and flow cytometry–based analysis (F). (C and G–I) Cells were treated with the indicated reagents for 24 h. Levels of phosphorylated CREB (CREB-pS133) were assessed by Western blot analyses and normalized to those of total CREB (C). Levels of AMPK-α-pT172 and AMPK-α1 were assessed by Western blot analyses and normalized to those of actin (G–I). Molecular mass is indicated in kilodaltons. a, P < 0.05 versus untreated STHdhQ109 cells; b, P < 0.05 versus untreated STHdhQ7 cells. (A–I) Data are presented as the mean ± SEM of three independent experiments.