Figure 4.
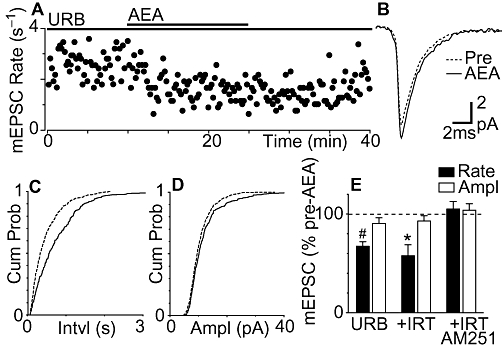
Fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) inhibition unmasks CB1 receptor-mediated inhibition of miniature excitatory postsynaptic currents (EPSCs) by anandamide. (A) Time course of miniature EPSC rate during superfusion of anandamide (AEA, 30 µM) in a neuron pre-incubated with URB597 (URB, 1 µM). (B). Average traces of miniature EPSCs before (Pre) and during anandamide, in the presence of URB597. Cumulative distribution plots of miniature EPSC (C) inter-event interval and (D) amplitude, before and during anandamide, in the presence of URB597. (E) Bar chart of the mean rate and amplitude (Ampl) of miniature EPSCs during application of anandamide, in neurons pre-incubated in URB597 alone (n = 6), URB597 plus iodoresiniferatoxin (IRT, 300 nM, n = 5), or URB597 plus AM251 (3 µM, n = 6). Data in (E) are expressed as a percentage of the pre-anandamide level (averaged across all neurons tested); *P < 0.05, #P < 0.0001, significantly different from values before AEA. (A–D) are taken from the same neuron.
